Types of Software
Software is instructions, programs to execute and it is classified as
System Software – It has direct interface with hardware Windows XP, Linux and consist of
Operating System Software – It controls the hardware and running of the application software like Linux, Windows XP/2003, MS-DOS. It does resource (CPU, memory) and task management with command interpretation (by a user interface graphical or character).
Application Software –It needs system software and it fulfill a specific user’s requirement like
Word Processing Software – It create and edit letters, reports, etc. like MS-Word
Spreadsheet Software – It store and process data in columns and rows like MS-Excel.
Presentation Graphics Software – It is used to create slides for presentations like MS-PowerPoint.
SOFTWARE
Software is instructions for the computer. Microsoft Corporation, USA released the MS-DOS operating system then Windows 3.11, Windows 95, Windows 98 and then finally Windows XP (eXPerience) was released in 2001. New Windows versions are Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8. User interaction with computer is to issue instructions and can be in two forms
- CUI (Character User Interface) – Commands are given as in MS-DOS, UNIX and LINUX.
- GUI (Graphical User Interface) – Commands are in graphics called icons like Windows XP.
Windows XP addressed many issues and added a number of improvements. The letters “XP” stand for “eXPerience,” meaning the operating system is meant to be a new type of user experience. Various parts of the interface are –
- The Desktop – Screen shown after Windows is loaded. It has icons, dialog box and pointer.
- Window – It is screen area with border around and has programs or files currently using.
- Icons – They are small graphic objects that represent specific programs to be used.
- Dialog box – Area of the screen within window that contains messages or input to be given.
- Mouse pointer – It shows where the mouse is currently pointing.
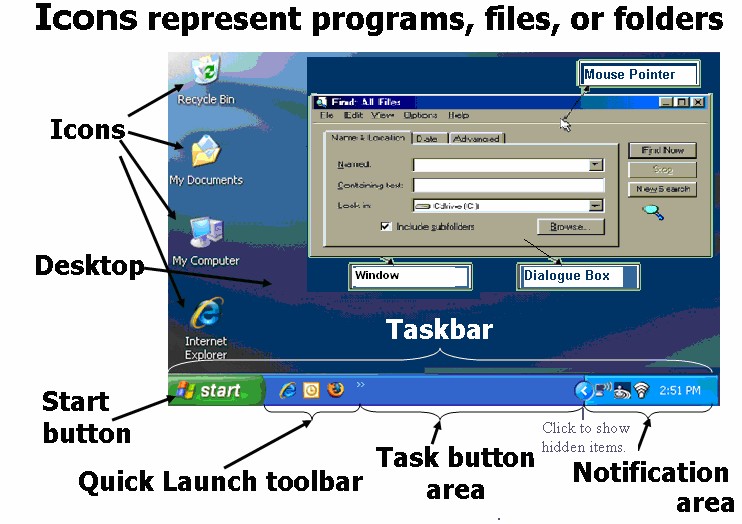
The Task Bar – It is a bar displayed at bottom to launch and monitor running applications. It has from left to right the Start menu button, Quick Launch bar, taskbar buttons, and notification area. The tasks on the task bar will expand or contract to fill the space depending upon the number of tasks and various parts of taskbar are –
Quick launch toolbar- It has shortcut to program to open on click. Windows gives default entries.
Task or Taskbar Button area – Windows places a button of program by user on the taskbar.
Notification area- It displays icons not shown on desktop for status. It has time and volume icon. It also shows printer icon, during printing. It is also called as the system tray.
The Start Button – It opens start menu on click, which is central point for application and tasks.
The Start Menu – It is a customizable nested list of programs for the user to launch and has
| Component | Use |
| My Documents | Windows default linking to a folder for storing user documents. |
| My Recent Documents | Sub menu listing files which were being worked upon recently. |
| All Programs | It lists all user or system programs to choose for running. |
| Control Panel | It helps in changing the settings of many windows features. |
| Printers & Faxes | It is a link in control panel for configuring printer & fax. |
| Search | It is used to search for a file or folder on a computer or on network. |
| Help & Support | Opens windows help facility, to review topics from a table of contents. |
| Run | Type the path and filename of a program, file, or folder to open. |
| Turn Off Computer | Prepares your computer to be turned off or Log Off or Restart. |
An arrowhead on the right indicates a sub menu. The Run option has three dots indicating a dialog box will open, asking you to enter the command you want to run if you select it.
Parts of a Window
Screen area to display output of or allow input to one or more processes. It usually has a rectangular shape that can overlap with the area of other windows and can be arranged on a desktop. They can be manipulated with a mouse cursor or even keyboard. They can be resized, moved, restored or closed. Windows usually include a menu-bar, toolbars, controls, icons and often a working area.
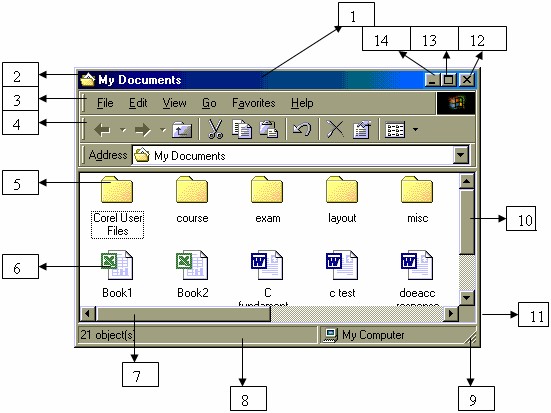
| No. | Part | Use |
| 1 | Title Bar | Name of the program and to move window |
| 2 | Control Menu Icon | Opens control menu to move, size or close the window |
| 3 | Menu Bar | Contains the drop down menus that are available in the window |
| 4 | Toolbar | Contains tools related to the contents of the window. |
| 5 | Folder Icon | Represents a folder which can contain other folders or files |
| 6 | File Icon | Represents a folder which contain other folders or files |
| 7 | Horizontal Scroll Bar | Allows moving the contents of windows horizontally |
| 8 | Status Bar | Provides information about what is selected in the window. |
| 9 | Sizing Handle | Allows sizing of the window in two dimensions |
| 10 | Vertical Scroll Bar | Allows moving the contents of the windows Vertically |
| 11 | Window Border | Separates window from desktop and is used to size the window |
| 12 | Close Button | Closes the window |
| 13 | Maximize Button | Increases the size of the window to fill the desktop |
| 14 | Minimize Button | Decreases size of the window to see other windows or desktop. |
Windows Explorer and Control Panel
Windows explorer shows files, folders, drives and their content in two panes – left or explorer and right or content pane. Left pane shows hierarchical (tree) structure of devices and folders in the system. Right pane shows the content of item selected in left pane. Explorer pane has “+” icon along with folder to expand or collapse them. It gives a graphical view of all local and networked resources and can copy move rename and search for files and folders.
| Folder part | What it’s useful for |
| Address bar | Used to navigate to a different folder without closing the current folder window. |
| Back and Forward buttons | Use to navigate to other folders already opened without closing the current window and work in conjunction with the Address bar |
| Search box | Type a word in Search box to look for a file or subfolder stored in current folder. |
| Toolbar | It is to perform common tasks like copying files, deleting folders, etc. |
| Navigation pane | It changes view to other folders. If a folder is visited often, drag that folder to the Navigation pane to make it your favorite links. |
| File list | The contents of current folder are displayed. |
| Column headings | Changes how files in file list are organized and can sort, group, or stack the files in the current view. |
| Details pane | Shows most common properties associated with the selected file like the author, the date file last changed and any descriptive tags of the file. |
| Preview pane | It displays contents of many kinds of files like pictures, etc. |
The Control Panel
Various options of a control panel which can be configured are
| Control Panel Item | Used For |
| Accessibility Options | Set keyboard or mouse for disabled persons. |
| Add New Hardware | Installation of new hardware like CD-ROM, display adapters, etc. |
| Add /Remove Programs | Add or remove Ms-Windows modules or application software. |
| Date and Time | Sets date and time and also the time zone. |
| Display | Sets colors and fonts for screen elements, picture for desktop, screen saver, screen resolution, display driver and energy saving mode. |
| Fonts | Adds and deletes typefaces for screen display and printer output. |
| Keyboard | Sets cursor blink rate, keyboard language and type of keyboard. |
| Mouse | Sets mouse’s pointer speed, swap between left and right buttons and shape of various pointers. |
| Network Connections | Configures network (hardware and software), network identification. |
| Power Options | Applicable if battery powered, it shows of battery charge condition. |
| Printers and Faxes | Modify properties of installed printers and install new printer also. |
| Regional Settings | Sets how Window displays time, date, numbers and currency. |
| Sounds & Audio Devices | Turns on or off sound on events, changes the audio, MIDI, CD music and other multimedia device drivers setting and properties, if installed. |
| System | Give details on system’s internal devices, can optimize system performance and also a number of system troubleshooting options. |

