Model–view–controller is an architectural pattern commonly used for developing user interfaces that divides an application into three interconnected parts. This is done to separate internal representations of information from the ways information is presented to and accepted from the user. The MVC design pattern decouples these major components allowing for efficient code reuse and parallel development.
Traditionally used for desktop graphical user interfaces (GUIs), this architecture has become popular for designing web applications and even mobile, desktop and other clients. Popular programming languages like Java, C#, Ruby, PHP and others have popular MVC frameworks that are currently being used in web application development straight out of the box.
As with other software patterns, MVC expresses the “core of the solution” to a problem while allowing it to be adapted for each system. Particular MVC architectures can vary significantly from the traditional description here.
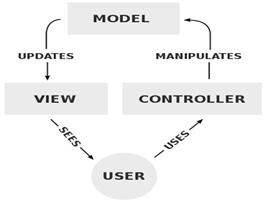
Components
- The model is the central component of the pattern. It expresses the application’s behavior in terms of the problem domain, independent of the user interface. It directly manages the data, logic and rules of the application.
- A view can be any output representation of information, such as a chart or a diagram. Multiple views of the same information are possible, such as a bar chart for management and a tabular view for accountants.
- The third part or section, the controller, accepts input and converts it to commands for the model or view.
Interactions
In addition to dividing the application into three kinds of components, the model–view–controller design defines the interactions between them.
- The model is responsible for managing the data of the application. It receives user input from the controller.
- The view means presentation of the model in a particular format.
- The controller responds to the user input and performs interactions on the data model objects. The controller receives the input, optionally validates it and then passes the input to the model.
Evolution
One of the seminal insights in the early development of graphical user interfaces, MVC became one of the first approaches to describe and implement software constructs in terms of their responsibilities.
Trygve Reenskaug introduced MVC into Smalltalk-76 while visiting the Xerox Palo Alto Research Center (PARC) in the 1970s. In the 1980s, Jim Althoff and others implemented a version of MVC for the Smalltalk-80 class library. Only later did a 1988 article in The Journal of Object Technology (JOT) express MVC as a general concept.
The MVC pattern has subsequently evolved, giving rise to variants such as hierarchical model–view–controller (HMVC), model–view–adapter (MVA), model–view–presenter (MVP), model–view–view model (MVVM), and others that adapted MVC to different contexts.
The use of the MVC pattern in web applications exploded in popularity after the introduction of NeXT’s WebObjects in 1996, which was originally written in Objective-C (that borrowed heavily from Smalltalk) and helped enforce MVC principles. Later, the MVC pattern became popular with Java developers when WebObjects was ported to Java. Later frameworks for Java, such as Spring (released in October 2002), continued the strong bond between Java and MVC. The introduction of the frameworks Django (July 2005, for Python) and Rails (December 2005, for Ruby), both of which had a strong emphasis on rapid deployment, increased MVC’s popularity outside the traditional enterprise environment in which it has long been popular. MVC web frameworks now hold large market-shares relative to non-MVC web toolkits.
Web Application and MVC
Although originally developed for desktop computing, MVC has been widely adopted as an architecture for World Wide Web applications in major programming languages. Several web frameworks have been created that enforce the pattern. These software frameworks vary in their interpretations, mainly in the way that the MVC responsibilities are divided between the client and server.
Some web MVC frameworks take a thin client approach that places almost the entire model, view and controller logic on the server. This is reflected in frameworks such as Django, Rails and ASP.NET MVC. In this approach, the client sends either hyperlink requests or form submissions to the controller and then receives a complete and updated web page (or other document) from the view; the model exists entirely on the server. Other frameworks such as Angular JS, Ember JS, JavaScript MVC and Backbone allow the MVC components to execute partly on the client
Advantages
- Simultaneous development – Multiple developers can work simultaneously on the model, controller and views.
- High cohesion – MVC enables logical grouping of related actions on a controller together. The views for a specific model are also grouped together.
- Low coupling – The very nature of the MVC framework is such that there is low coupling among models, views or controllers
- Ease of modification – Because of the separation of responsibilities, future development or modification is easier
- Multiple views for a model – Models can have multiple views
Disadvantages
- Code navigability – The framework navigation can be complex because it introduces new layers of abstraction and requires users to adapt to the decomposition criteria of MVC.
- Multi-artifact consistency – Decomposing a feature into three artifacts causes scattering. Thus, requiring developers to maintain the consistency of multiple representations at once.
- Pronounced learning curve – Knowledge on multiple technologies becomes the norm. Developers using MVC need to be skilled in multiple technologies.

