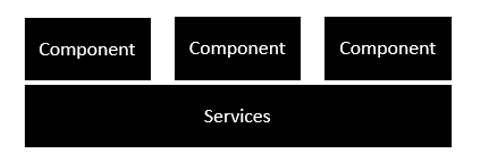
The below image shows the anatomy of an Angular application. Each application consists of Components. Each component is a logical boundary of functionality for the application. You need to have layered services, which are used to share the functionality across components.
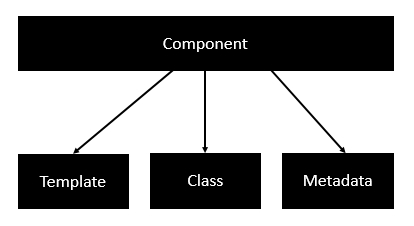
Following is the anatomy of a Component. A component consists of −
- Class − This is like a C++ or Java class which consists of properties and methods.
- Metadata − This is used to decorate the class and extend the functionality of the class.
- Template − This is used to define the HTML view which is displayed in the application.
Following is an example of a component.
import { Component } from ‘@angular/core’;
@Component ({
selector: ‘my-app’,
templateUrl: ‘app/app.component.html’
})
export class AppComponent {
appTitle: string = ‘Welcome’;
}
Each application is made up of modules. Each Angular 2 application needs to have one Angular Root Module. Each Angular Root module can then have multiple components to separate the functionality.
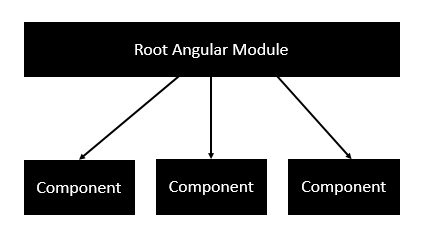
Following is an example of a root module.
import { NgModule } from ‘@angular/core’;
import { BrowserModule } from ‘@angular/platform-browser’;
import { AppComponent } from ‘./app.component’;
@NgModule ({
imports: [ BrowserModule ],
declarations: [ AppComponent ],
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ]
})
export class AppModule { }
Each application is made up of feature modules where each module has a separate feature of the application. Each Angular feature module can then have multiple components to separate the functionality.

