Absolute positioning can render an element to a particular place in a web page. Relative positioning is usually a part of the normal flow-positioning model, as the position of the element is relative to its position in the normal flow.
But absolute positioning takes the element out of the flow of the document, thus taking up no space. Other elements in the normal flow of the document will act as though the absolutely positioned element was never at that position.
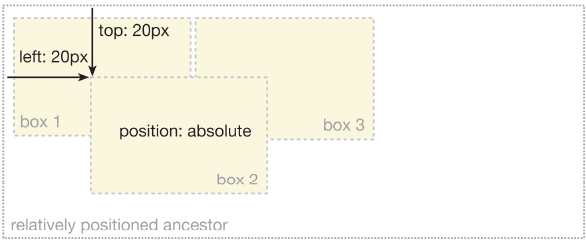
An absolutely positioned element is positioned in relation to its nearest positioned ancestor. If the element has no positioned ancestors, it will be positioned in relation to the initial containing block. Depending on the user agent, this will either be the canvas or the HTML element. As with relatively positioned boxes, an absolutely positioned box can be offset from the top, bottom, left, or right of its containing block and hence the element can be positioned anywhere on the web page.
But as absolutely positioned elements are taken out of the flow of the document, they can overlap
other elements on the page. Absolute positioning can be a useful tool when laying out a page, especially if it is done using relatively positioned ancestors.

