Various hadoop vendors are
Cloudera
Cloudera is the number 1 provider of Hadoop software and commercial support. From this position of strength, Cloudera has sought to advance the manageability, reliability and usability of the platform.
During 2012, the discussion turned from convincing the broad corporate market that Hadoop is a viable platform to convincing people that they can gain value from the masses of data on a cluster. But to do that, we’ll need to get past one of Hadoop’s biggest flaw: the slow, batch-oriented nature of MapReduce processing. Tackling the problem head on, Cloudera has introduced Impala, an interactive-speed SQL query engine that runs on the existing Hadoop infrastructure. Two years in development and now in beta, Impala promises to make all the data in the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and Apache HBase database tables accessible for real-time querying. Unlike Apache Hive, which offers a degree of SQL querying of Hadoop, Impala is not dependent on MapReduce processing, so it should be much faster.
Cloudera was the first company to be formed to build enterprise solutions based on Hadoop. Cloudera has a Hadoop distribution known as Cloudera’s Distribution for Hadoop (CDH). Here is a simplified representation of Cloudera’s Hadoop Ecosystem.
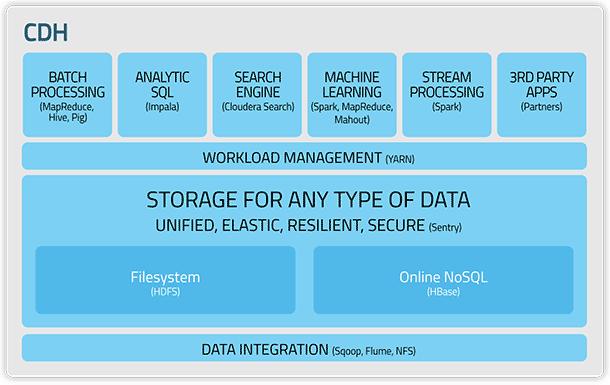
Cloudera’s Hadoop Ecosystem includes the following features/components: Apache Avro, Apache Crunch, Apache DataFu, Apache Flume, Apache Hadoop, Apache Hbase, Apache Hive, Hue, Cloudera Impala, Kite SDK (formerly CDK), LLAMA, Apache Mahout, Apache Oozie, Parquet, Apache Pig, Cloudera Search, Apache Sentry, Apache Spark, Apache Sqoop and Apache ZooKeeper.
Here are few highlights of CDH
- CDH can be deployed on-premise as well as in the cloud.
- Cloudera manager simplifies the deployment and management of Hadoop and other components in Cloudera’s Hadoop Ecosystem.
- Cloudera has an Enterprise edition – Cloudera Enterprise, and is proprietary. There three variations of this – Basic, Flex, and Data Hub.
- Express edition is available via a free download.
- Cloudera Enterprise Data Hub edition is supported on AWS cloud.
Hortonworks
Hortonworks is the youngest provider of Hadoop software and commercial support, but it’s an old hand when it comes to working with the platform. The company is a 2011 spinoff of Yahoo, which remains one of the world’s largest users of Hadoop. In fact, Hadoop was essentially invented at Yahoo, and Hortonworks retained a team of nearly 50 of its earliest and most prolific contributors to Hadoop.
Hortonworks released its first product, Hortonworks Data Platform (HDP) 1.0, in June. Unlike those from rivals Cloudera and MapR, Hortonworks’ distribution is entirely of open source Apache Hadoop software. The company led the development of the HCatalog table management service, which is aimed at the problem of doing analytics against the data in Hadoop.
Here is a simplified representation of Hortonworks Data Platform.
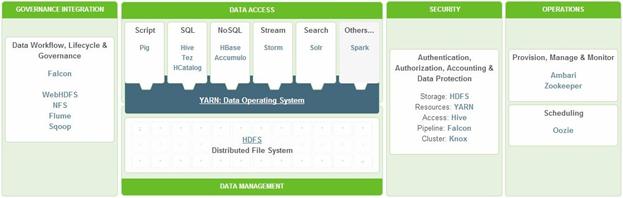
Hortonworks Data Platform includes the following features/components: Apache Hadoop, Apache Pig, Apache Hive, Apache Hbase, Apache ZooKeeper, Apache Oozie, Apache Sqoop, Apache Flume, Apache Ambari, Hue, Apache Mahout, Apache Knox, Apache Storm, Apache Tez, Apache Phoenix, Apache Accumulo and Apache Falcon.
Here are few highlights of Hortonworks Data Platform:
- Can be deployed on-premise as well as in the cloud.
- Supports deploying on Linux as well Windows platforms.
- HDP is built in open through Apache Projects.
MapR
MapR’s guiding principles are practicality and performance, so it didn’t think twice about chucking the Hadoop Distributed File System out of its Hadoop software distribution. HDFS had (and still has, MapR argues) reliability and availability flaws, so MapR uses the proven Network File System (NFS) instead.
MapR’s latest quest for better performance (regardless of open source consequences) is the M7 software distribution, which the vendor says delivers high-performance Hadoop and HBase in one deployment. MapR also uses its proprietary infrastructure to support snapshotting, high availability and system recovery for HBase.
Below is a simplified architecture of MapR Data Platform.
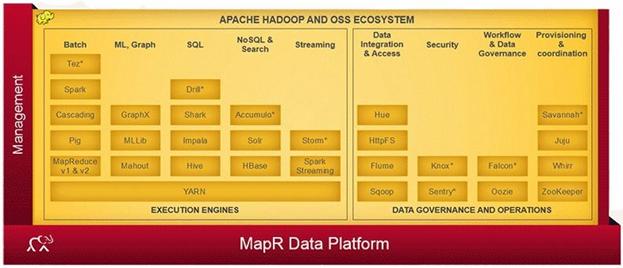
Here are few highlights of MapR:
- MapR is available in the cloud through some of the leading cloud providers – Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Compute Engine, CenturyLink Technology Solutions, and OpenStack.
- MapR integrates/supports more than 20 open source projects.
- MapR supports multiple versions of various individual projects it integrates into its data platform. This gives the users flexibility to migrate to the subsequent/latest versions at their own pace.
Amazon EMR
Amazon is about as big a big data practitioner as you can get. It’s also the leading big data services provider. It introduced Elastic MapReduce (EMR) based on Hadoop, EMR isn’t just a service for MapReduce sand boxes; it’s being used for day-to-day high-scale production data processing by businesses including Ticketmaster and DNA researcher Ion Flux.
Amazon Web Services upped the big data ante in 2012 with two new services: Amazon DynamoDB, a NoSQL database service, and Amazon Redshift, a scalable data warehousing service now in preview and set for release early next year.
These three services are cornerstones for exploiting big data, and don’t forget Amazon’s scalable S3 storage, EC2 compute capacity and myriad integration and connection options for corporate data centers. In short, Amazon has been a big data pioneer, and its services appeal to more than just startups, SMBs and Internet businesses.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic MapReduce (EMR) was among the first Hadoop offerings available in the market. Here is a high-level architecture/job flow of Amazon EMR.
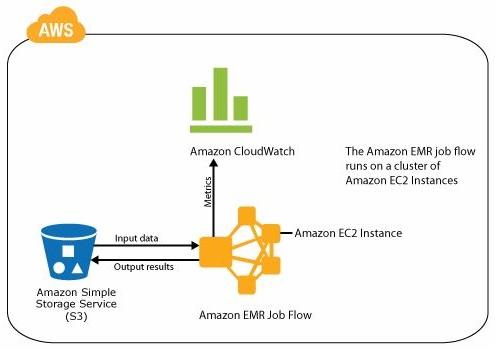
Amazon EMR contains most of the popular features/components like Hive, Pig, HBase, DistCp, Ganglia, etc. integrated into it.
Here are few highlights of Amazon EMR:
- EMR is a Hadoop distribution in the Cloud.
- Leverages AWS’s Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) for computation.
- Leverages AWS’s Simple Storage Service (S3) for storage.
- Is tightly integrated with other AWS services.
- Deployment and Management is simplified using AWS Management Console and AWS Toolkit.

