Understanding Scrum
In this section, we will be understanding scrum, along with its benefits and weaknesses.
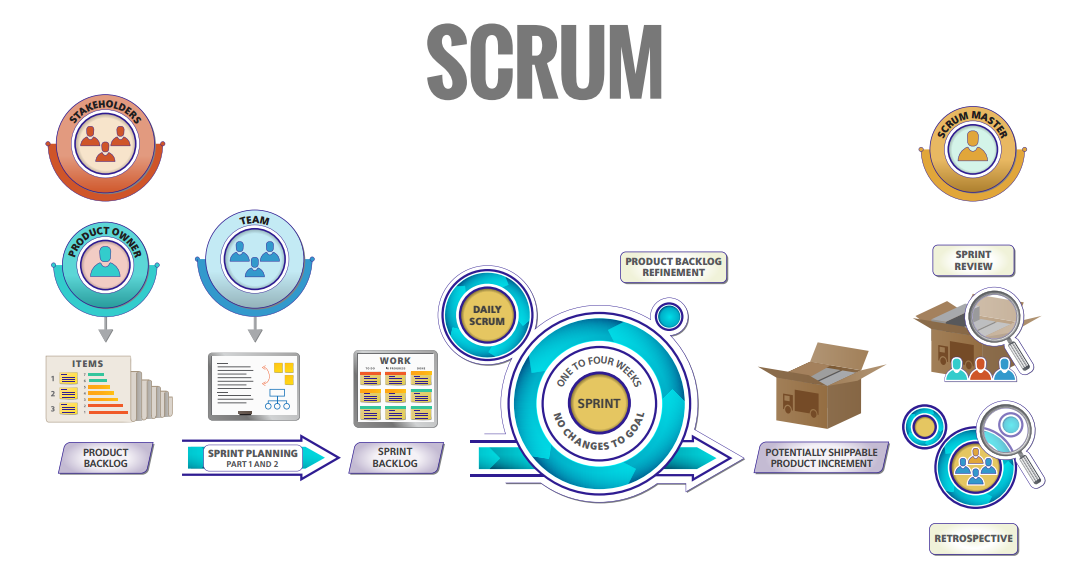
Scrum refers to a lightweight agile method that uses practices, events, roles, artifacts, and rules for project execution. Further, there are three ”pillars” to support and guide all facets of the Scrum project:
- Transparency: First things first, everything on a Scrum project is visible to all who have a stake in the end product. Moreover, the outcome of Scrum is transparent and visible to stakeholders. Therefore, it fosters a very open and collaborative culture. For example the use of burndown charts, impediments log, convention of daily stand-up meetings, or a ‘definition-of-done’ between the development team and the user accepting the work.
- Inspection: Secondly, the Scrum project undergoes evaluation on a regular basis to ensure that progress towards the goals and objectives. Examples of opportunities for inspection is sprint reviews and sprint retrospectives. Further, during these events, the project team inspects and reflects on the project metrics like user feedback.
- Adaptation: Thirdly, the Scrum project is quite adaptive. In other words, processes are adjusted as any undesirable issue occurs. Moreover, Adaptation is the ‘secret sauce’ of how Scrum teams continuously strive for improvement.
The benefits of Scrum include the following:
- The process is incremental and iterative.
- In addition, requirements are permitted to change over a period of time.
The weaknesses of Scrum methods include the following:
- For instance, if a team member leaves the project, then the impact is significant.
- The Scrum project requires skillful team members. Team members who lack skills and knowledge can lead to project delays.
Scrum Master
Scrum Master facilitates scrum and is accountable for removing impediments to the ability of the team to deliver the product goals and deliverables. The scrum master is not a project manager, however, it acts as a shield between the team and any distracting influences. Further, it helps to ensure the team follows the agreed processes in the Scrum framework, often facilitates key sessions, and encourages the team to improve.
The key responsibilities of a scrum master incorporates the following:
- Helping the team to determine the definition of done for the product, with input from key stakeholders
- Coaching the team, within the Scrum principles, in order to deliver high-quality features for its product
- Coaching the development team in self-organization and cross-functionality
Scrum Tools
Like other agile methods, effective adoption of Scrum cis associated with a wide range of tools. Many companies use universal tools, such as spreadsheets to create as well as maintain the facts such as the sprint backlog. Moreover, they are open-source and proprietary software packages for Scrum.
On the other hand, other organizations implement Scrum without any software tools and maintain them in hard-copy forms.
Get certified and unlock more opportunities. Practice and Validate your skills to become a Certified Agile Testing Professional Now!

