Skills Needed
Technical and personal kills are essential requirement for being an ethical hacker.
Technical skills include computing skills, being knowledgeable about computer programming, networking, web programming, database and operating systems. In-depth knowledge about targeted platforms whether Windows, Unix or Linux is also essential. Sometimes the ethical hacker is a part of a team, hired to test network and computer systems and find vulnerabilities due to specialization in specific skill set. A strong command of countermeasures to prevent attacks is also required for post-attack remedial and prevention action.
Personal skills include patience, persistence, and immense perseverance due to variable time and level of concentration needed for successful attack.
Stages of Hacking
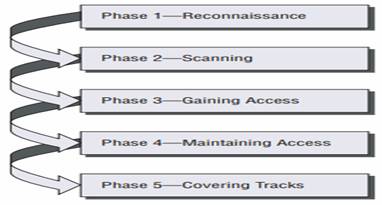
Phases of hacking are usually summarized in distinct phases of preparation (formal contract is signed with non-disclosure and legal clause to protect the ethical hacker against any prosecution. The contract also outlines infrastructure perimeter, evaluation activities, time schedules and resources available), conduct (evaluation technical report is made after testing vulnerabilities) and conclusion (results of the evaluation is communicated to the sponsors and corrective advise is taken if needed.). Hacking can be detailed in five distinct stages which are
Reconnaissance – It is the longest phase which may last weeks or months. This phase needs variety of sources to learn and gather information about the target which includes
- Internet searches
- Social engineering
- Dumpster diving
- Domain name management/search services
- Non-intrusive network scanning
These activities cannot be easily defended against as information about an organization or business finds its way to the Internet via various routes. Employees are often easily tricked into providing tidbits of information which, over time, act to complete a complete picture of processes, organizational structure, and potential soft-spots. Computing infrastructure should not leak following information
- Software versions and patch levels
- Email addresses
- Names and positions of key personnel
- Ensure proper disposal of printed information
- Provide generic contact information for domain name registration lookups
- Prevent perimeter LAN/WAN devices from responding to scanning attempts
Scanning – After gathering enough information about working of the business and enlisting information of value, ethical hacker begins the process of scanning perimeter and internal network devices looking for weaknesses, including
- Open ports
- Open services
- Vulnerable applications, including operating systems
- Weak protection of data in transit
- Make and model of each piece of LAN/WAN equipment
Scans of perimeter and internal devices can often be detected with intrusion detection (IDS) or prevention (IPS) solutions, but not always. Possible steps to thwart such scans are
- Shutting down all unneeded ports and services
- Allow critical devices, or devices housing or processing sensitive information, to respond only to approved devices. Closely manage system design, resisting attempts to allow direct external access to servers except under special circumstances and constrained by end-to-end rules defined in access control lists
- Maintaining proper patch levels on endpoint and LAN/WAN systems
Gaining Access – Gaining access to resources is the aim of hacking attacks, either for extracting information of value or use the network as a launch site for attacks against other targets. Hence, the attacker must have some access to one or more network devices.
In addition to above defensive steps, security staff should also ensure end-user devices and servers are not easily accessible by unauthenticated users by denying local administrator access to business users and closely monitoring domain and local admin access to servers. Physical security controls also detect attempts and delay an intruder to allow effective internal or external manual response (i.e., security guards or law enforcement). Encrypting highly sensitive information and protecting keys is also crucial step to undertake. Even wit weak network security, scrambled information and denying attacker access to encryption keys is also a good defense. But other than encryption, other risks of weak security are system unavailability or use of your network in the commission of a crime.
Maintaining Access – Having gained access, an attacker must maintain access long enough to accomplish his or her objectives. Although an attacker reaching this phase has successfully circumvented your security controls, this phase can increase the attacker’s vulnerability to detection. In addition to using IDS and IPS devices to detect intrusions, you can also use them to detect extrusions. The list of intrusion/extrusion detection methods includes
- Detect and filter file transfer content to external sites or internal devices
- Prevent/detect direct session initiation between servers in your data center and networks/systems not under your control
- Look for connections to odd ports or nonstandard protocols
- Detect sessions of unusual duration, frequency, or amount of content
- Detect anomalous network or server behavior, including traffic mix per time interval
Covering Tracks – After achieving the objectives of attack, the ethical hacker takes steps to hide the intrusion and possible controls left behind for future visits. Hence, other than the anti-malware, personal firewalls, and host-based IPS solutions, deny business users local administrator access to desktops. Alert on any unusual activity, any activity not expected as per the working of the business.