It is the most widely used strategy for statistical quality assurance, uses data and statistical analysis to measure and improve a company’s operational performance, it Identifies and eliminates defects in manufacturing and service-related processes. It is basically a method that provides organizations tools to improve the capability of their business processes. This increase in performance and decrease in process variation lead to defect reduction and improvement in profits, employee morale, and quality of products or services.
The Six Sigma concept was developed at Motorola in the 1980s. Six Sigma can be viewed as a philosophy, a technique, or a goal.
- Philosophy – Customer-focused breakthrough improvement in processes
- Technique – Comprehensive set of statistical tools and methodologies
- Goal – Reduce variation, minimize defects, shorten the cycle time, improve yield, enhance customer satisfaction, and boost the bottom line
Mathematical Six Sigma
The term ‘Six Sigma’ is drawn from the statistical discipline ‘process capability studies’. Sigma, represented by the Greek alphabet ‘σ’, stands for standard deviation from the ‘mean’. ‘Six Sigma’ represents six standard deviations from the ‘mean.’ This implies that if a company produces 1,000,000 parts/units, and its processes are at Six Sigma level, less than 3.4 defects only will result. However, if the processes are at three sigma level, the company ends up with as many as 66,807 defects for every 1,000,000 parts/units produced.
The table below shows the number of defects observed for every 1,000,000 parts produced (also referred to as defects per million opportunities or DPMO).
| Sigma Level | Defects per million opportunities |
| Two Sigma | 308,507 DPMO |
| Three Sigma | 66,807 DPMO |
| Four Sigma | 6,210 DPMO |
| Five Sigma | 233 DPMO |
| Six Sigma | 3.4 DPMO |
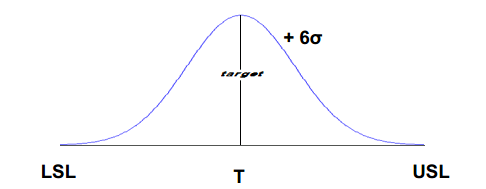
Process standard deviation (σ) should be so minimal that the process performance should be able to scale up to 12σ within the customer specified limits. So, no matter how widely the process deviates from the target, it must still deliver results that meet the customer requirements. Few terms used are
- USL – It is upper specification limit for a performance standard. Any deviation beyond this is a defect.
- LSL – It is lower specification limit for a performance standard. Any deviation below this is a defect.
- Target – Ideally, this will be the middle point between USL and LSL.
Six Sigma approach is to find out the root causes of the problem, symbolically represented by Y = F(X). Here, Y represents the problem that occurs due to cause (s) X.
| Y | x1, x2, x3, …., xn |
| Dependent | Independent |
| Customer related output | Input-process |
| Effect | Cause |
| Symptom | Problem |
| Monitor | Control |

