Certify and Increase Opportunity.
Be
Govt. Certified E-Commerce Professional
Security tools for authentication and authorization
Various security technologies and tools are used to secure information moving on internet and which usually includes
Cryptography
Cryptography is the practice and study of encryption and decryption — encoding data so it can only be decoded by intended recipients and rendered unreadable for others. There are two forms of encryption which are symmetric and asymmetric.
- Symmetric – Both sender and recipient know a common key used to encrypt and decrypt messages. Because the keys are same for both encrypting and decrypting, it is known as symmetric encryption. One benefit of this method is, that it requires significantly less resources in terms of CPU cycles to encrypt and decrypt the data but with a disadvantage being, both the sender and receiver must share the key in a secure way. If it is leaked to a third party, the entire mechanism becomes futile.
- Asymmetric – Two different but related keys are used in such a way that one key, called a private key, is kept as a secret, while the other public key is available to anyone. The two fundamental principles that drive this method are that, one key cannot be deduced from the other and messages encrypted with one key can only be decrypted by the other and vice versa. Advantage of this method is that it completely eliminates the need to securely share the keys, as a sender can use the recipient’s public key to encrypt the message, which can be read only by the recipient using his or her secure private key. But it has the disadvantage of being computationally expensive.
Firewall
It is a software or hardware-based security mechanism which controls the incoming and outgoing network traffic by analyzing the data packets and determining whether it should be allowed through or not, based on a rule set. A firewall establishes a barrier between two networks i.e. a trusted, secure internal network usually LAN and another network usually the Internet or WAN.
There are several types of firewall
- Packet filter: Looks at each packet entering or leaving the network and accepts or rejects it based on user-defined rules. Packet filtering is fairly effective and transparent to users, but it is difficult to configure. In addition, it is susceptible to IP spoofing.
- Application gateway: Applies security mechanisms to specific applications, such as FTP and Telnet servers. This is very effective, but can impose a performance degradation.
- Circuit-level gateway: Applies security mechanisms when a TCP or UDP connection is established. Once the connection has been made, packets can flow between the hosts without further checking.
- Proxy server: Intercepts all messages entering and leaving the network. The proxy server effectively hides the true network addresses.
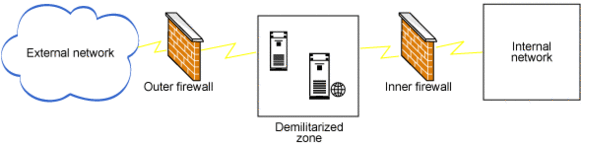
DMZ
DMZ or Demilitarized Zone also called as perimeter network is a physical or logical sub-network that contains and exposes an organization’s external-facing services to WAN or internet. It is used to offer a significant amount of services to the external network. You place the externally accessible servers in a demilitarized zone (DMZ) surrounded by firewalls on either side of the network. You configure the inner firewall more restrictively than the other firewall. Any communication from the external network to the internal network happens only through the servers deployed in the DMZ.
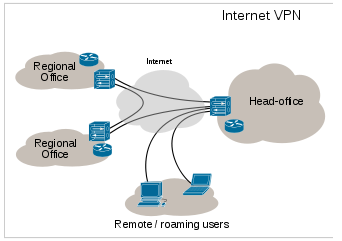
VPN
VPN or Virtual Private Network, is a private network that usually the Internet to connect remote sites or users together. It enables a computer to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if it were directly connected to the private network.
A VPN works by using the shared public infrastructure while maintaining privacy through security procedures and tunneling protocols such as the Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP). In effect, the protocols, by encrypting data at the sending end and decrypting it at the receiving end, send the data through a “tunnel” that cannot be “entered” by data that is not properly encrypted. An additional level of security involves encrypting not only the data, but also the originating and receiving network addresses.
VPN is classified by
- the protocols used to tunnel the traffic.
- the tunnel’s termination point location, e.g., on the customer edge or network-provider edge.
- whether they offer site-to-site or remote-access connectivity.
- the levels of security provided.
- the OSI layer they present to the connecting network, like Layer 2 or Layer 3.
Apply for E-commerce Certification Now!!
https://www.vskills.in/certification/web-development/certificate-in-e-commerce

