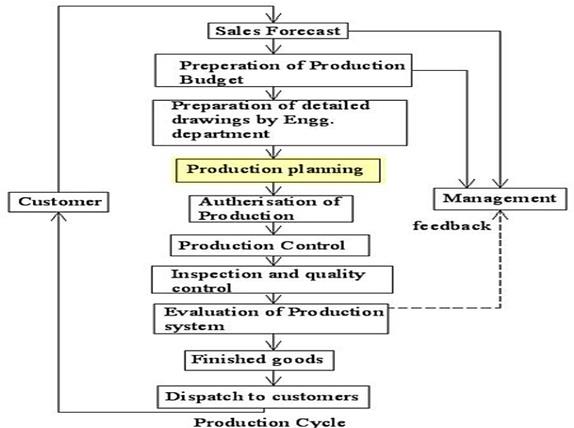
The PPC Cycle refers to Production Planning Control. It has 3 phases—preplanning, planning, controlling. The Pre-Planning Phase consists of product development, sales forecasting, factory or plant layout, equipment selection policy, and preplanning of production just prior to large scale production. The Planning Phase consists of planning of the 4 M’s (methods, materials, men and machines), routing, estimating, scheduling, and dispatching. The Controlling Phase consists of follow up, inspecting, and evaluating.
At its core, production planning represents the beating heart of any manufacturing process. Its purpose is to minimize production time and costs, efficiently organize the use of resources and maximize efficiency in the workplace.
Production planning incorporates a multiplicity of production elements, ranging from the everyday activities of staff to the ability to realize accurate delivery times for the customer. With an effective production planning operation at its nucleus, any form of manufacturing process has the capability to exploit its full potential.
Objectives of Production Planning Control
The ultimate objective of production planning and control, like that of all other manufacturing controls, is to contribute to the profits of the enterprise. As with inventory management and control, this is accomplished by keeping the customers satisfied through the meeting of delivery schedules. Specific objectives of production planning and control are to establish routes and schedules for work that will ensure the optimum utilization of materials, workers, and machines and to provide the means for ensuring the operation of the plant in accordance with these plans.

