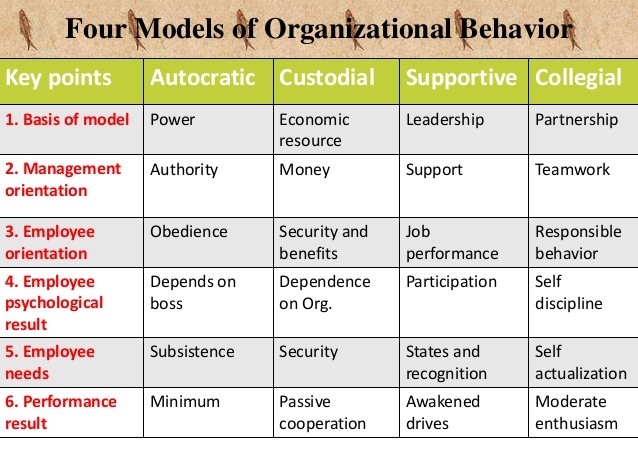
Every organization develops a particular model in which Behavior of the people takes place. This model is developed on the basis of management’s assumptions about people and the vision of the management. There are five model of organizational Behavior, such as
- Autocratic
- Custodial
- Supportive
- Collegial
Autocratic Model
In the autocratic model, managerial orientation is towards power. Managers see authority as the only means to get the things done, and employees are expected to follow orders. The result is high dependence on boss. This dependence is possible because employees live on the subsistence level. The organizational process is mostly formalized; the authority is delegated by right of command over people to whom it applies. The management decides what the best action for the employees is. A very strict and close supervision is required to obtain desirable performance from them. The autocratic model represents traditional thinking which is based on the economic concept of the man. With the changing values and aspiration levels of people, this model is yielding place to others. However, this does not mean that this model is discarded in total. In many cases; the autocratic model of organizational Behavior may be a quite useful way to accomplish performance, particularly where the employees can be motivated by physiological needs. This generally happens at lower strata of the organization.
Custodial Model
In the custodial model, the managerial orientation is towards the use of money to play for employee benefits. The model depends on the economic resources of the organization and its ability to pay for the benefits. While the employees hope to obtain security, at the same time they become highly dependent on the organization. An organizational dependence reduces personal dependence on boss. The employees are able to satisfy their security needs or in the context of Herzberg’s theory only maintenance factors. These employees working under custodial model feel happy, their level of performance is not very high. Since employees are getting adequate regards and organizational security, they feel happy. However, they are not given any authority to decide what benefits or rewards they should get. Such an approach is still quite common in many business organizations in India. The phenomenon is more predominant in family-managed business organizations where family characteristics have also been applied to the organizational settings. The basic ingredient of the family-managed system is that, parents decide what is good or bad for their children and managers decide what is good for their employees. From this point of view, this model is not suitable for matured employees.
Supportive Model
The supportive model organizational Behavior depends on managerial leadership rather than on the use of power of money. The aim of managers is to support employees in their achievement of results. The focus is primarily on participation and involvement of employees in managerial decision-making process. The supportive model is based on the assumptions that human beings move to the maturity level and they expect the organizational climate which supports these expectations. Various organizational processes-communication, leadership, decision-making, interaction, control, and influence-are such that, these help employees to fulfill their higher order needs such as esteem and self-actualization.
Supportive model is best suited in the conditions when employees are self-motivated. Thus, this emphasizes not on the economic resources of the organization but its human aspect. Manager’s role is to help employees to achieve their work rather than supervising them closely. This can be applied more fruitfully for higher level managers whose lower order needs are satisfied reasonably.
Organizations with sophisticated technology and employing professional people can also apply this model for getting best out of their human resources. However, this does not mean that, this model can be applied in all circumstances. It may not be the best model to apply in less developed nations. Because their employees need structures that are often at lower levels and their social conditions are different’. Morever, this model can be applied more fruitfully for managerial levels as compared to operative levels. As such, the tendency of modern management is to move towards supportive model, especially for their management groups.
Collegial Model
Collegial model is an extension of supportive model. The term collegial refers to a body of people having common purpose. Collegial model is based on the team concept in which each employee develops high degree of understanding towards others and shares common goals. The employee response to this situation is responsibility. Employees need little direction and control from management. Control is basically through self discipline by the team members. The organizational climate is quite conductive to self fulfillment and self-actualization. Collegial model tends to be more useful with unprogrammed work requiring Behavioral flexibility, an intellectual environment, and considerable job freedom.
The various models of organizational Behavior are based on the assumption of the human characteristics and how they can work best. Since situational variables are strong factors in determining the organizational processes, managers cannot assume that a particular model is best suitable for all purposes and for all situations. Rather all the models will remain in practice and that too with considerable success. These models are basically constructed around need hierarchy. Since need hierarchy is not similar for all the employees, the same model cannot be used for all of them. The need hierarchy changes with the level of a person in the organization, level of his education, level of maturity, personality factors and the type of work environment. Considering these factors, a particular model can be applied. Organization theorists have argued that there is a tendency to move towards the adoption of supportive model because in this case people may give their best because in other models they do not find conditions conducive to give their best performance. This is why managers are taking a number of steps to humanize their organizations, such as participation, morale building, and so on to make the organizations more effective.