The loss given default (LGD) has a direct correlation to the collateralized portion as well as the cost of selling the collateral. The estimated value and type of collateral also have to be considered in developing the credit approval method. The LGD is the ratio of the loss on an exposure caused by the default of the counterparty to the amount outstanding at default. This ratio is calculated by businesses following the Internal Ratings-Based Approach (IRBA) for their retail portfolios. The estimated LGDs are necessary for the capital requirement of the institute because of incurred credit risk. The pricing process of credits is also highly affected by an accurate estimation of possible losses.
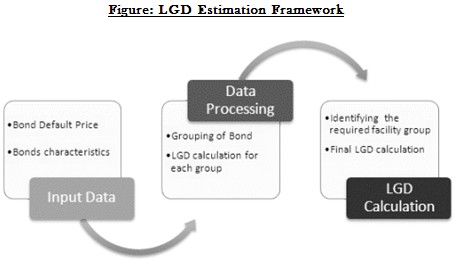
The methodology involves grouping of the bonds having similar characteristics and then dividing them into different categories. Each category, corresponding to the respective age of the loan, is calculated based on the default price. LGD for each category is the average of all individual bonds’ LGD in that category. To calculate the LGD for a facility, the characteristics of the facility need to be analyzed, and then decide in which category the facility falls. The corresponding LGD will be linked to the facility.
Formula for the calculation of LGD
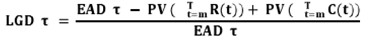
Where,
EAD = Exposure at Default
T = default time
m, t = start and finish points of the workout process respectively
PV(R(t)) = the recoveries during the workout process
PV(C(t)) = the costs during the workout process

