The overall layout design procedure can be considered to be composed of four phases viz.,
Phase I: Location
Phase II: General Overall Layout
Phase III: Detailed layout
Phase IV: Installation
Some important guidelines that help in the layout design are:
- Plan from whole to details
- First plan the ideal and then move to the practical aspects
- Material requirements should be central to the planning of process and machinery.
- Modify the process and machinery by different factors to plan the layout.
Though there is always an overlap in the different phases of layout design the major steps that have to be followed in the layout design are outlined as follows:
- Statement of the problem in terms of its objective, scope and factors to be considered
- Collection of basic data on sales forecasts, production volumes, production schedules, part lists, operations to be performed, work measurement, existing layouts, building drawings etc.
- Analysis of data and its presentation in the form of various charts
- Designing the production process
- Planning the material flow pattern and developing the overall material handling plan.
- Calculation of equipment requirements and work centers
- Planning of individual work centres
- Selection of material handling equipment
- Determining storage requirements
- Designing activity relationships
- Planning of auxiliary and service facilities
- Calculation of space requirements and allocation of activity areas
- Development of Plot Plan
- Development of Block Plan
- Development of detailed layouts in terms of steps (vii) to (xi)
- Evaluation, modification and checking of layouts
- Installation of layouts
- Follow up.
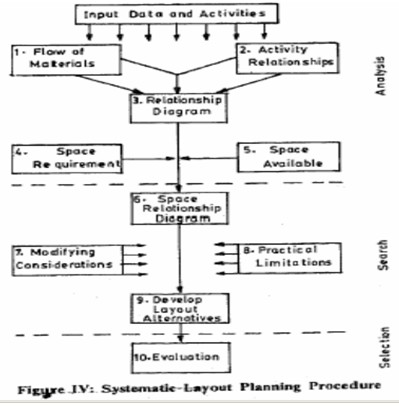
The S.L.P. (Systematic Layout Planning) procedure as presented by Francis and White (1974) is shown in Figure IV. We see that once the appropriate information is gathered, a flow analysis can be combined with an activity analysis to develop the relationship diagram. Space considerations when combined with the relationship diagram lead to the construction of the space relationship diagram. Based on the space relationship diagram, modifying considerations and practical limitations, a number of alternative layouts are designed and evaluated.