We can define innovation management as the management of innovation processes – both to product and organizational innovation. Innovation management involves a set of tools that assists the managers and engineers to have a common understanding of processes and goals. Innovation management allows the organization to respond to external or internal opportunities, and use its creativity to introduce new ideas, processes or products. Innovation management is not restricted to the research and development department, it involves workers at every level to contribute creatively to a company’s product development, manufacturing and marketing system.
Unfortunately, innovation is often misinterpreted with strategy. Strategy is all about achieving objectives, while innovation is about discovery where we never know exactly what can be achieved until we get there.
Pillars of Innovation
It is extremely hard to find novel solutions to important problems. Since it has been observed that there is always a list of important problems at any given time and with countless potential approaches to each one of them. In this case, innovation seems like too small a word.
Therefore, innovation is further divides into 3 categories
Competency
Since every organization has its own history and set of capabilities that helps determine its innovation competency. Where, it is impossible for an old-line industrial firm to operate like a hot Silicon Valley tech startup overnight. However, every enterprise can perform their best to improve.
Strategy
Since resource allocation is critical to strategy therefore it needs to be an integral part of aligning innovation to strategic objectives.
Management
It has been observed that even the most experienced firms which deploy resources sensibly still needs to manage innovation effectively. Where managing innovation becomes their primary focus.
Types of Innovation
Four categories of Innovation
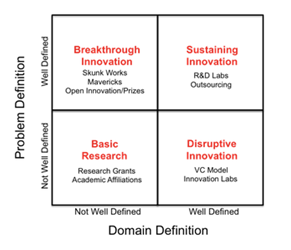
Basic Research
Basic research refers to the type of work done at universities or some R&D labs with no clearly defined outcome. Basic research focuses on discovering more about how things work. Often it has been said that basic research is not a type of innovation, since it does not necessarily result in a new product or service. Basic
Sustaining Innovation
Sustaining innovation is the type of innovation, where there is a clearly defined problem and a reasonably good understanding of how to solve it. For instance – “When Steve Jobs first envisioned the iPod, it was simply a device that allowed you to put “1000 songs in your pocket.” This innovation primarily required a certain amount of memory to fit into certain dimensions. Even though it was a difficult problem which took a few years to solve, but it was very clear what was involved and who was capable of solving them.
Disruptive Innovation
The concept of disruptive innovation was introduced Clayton Christensen – The Innovator’s Dilemma. This is primarily new approach to old products and services. Disruptive innovation is defined in the past as crappy innovation, as it tends to perform poorly on previously defined parameters (like early digital cameras that took lousy pictures), but outperform on a different parameter, such as price or convenience or compatibility.
Breakthrough Innovation
Breakthrough innovation is also referred as this “revolutionary science” by Thomas Kuhn as it involves a paradigm shift. In this case, the problem is well defined, but the path to the solution is unclear, usually because those involved in the domain have hit a wall.
Some of the examples of breakthrough innovation are transistors and discovery of the structure of DNA. By putting the parameters into two axes – Problem definition and Domain definition, following is the form a matrix that the four types of innovation fit nicely into.
Building an Innovative Culture
Building an innovative culture involves developing the ability to attract and nurture innovators a direct bearing on whether innovation can germinate and flourish in the organization. The main aim of the innovation leader is to create an innovation system. The team members must support innovation by leading projects and embodying the values of an innovative business culture.
As an innovation leader, you must focus on creating an environment that allows others to flourish in the following manner.
Expose employees to new ideas
It is always suggested to practice “cross-fertilization” by moving team members around from time to time and creating diverse teams. This not only encourages sharing of ideas but also expose employees to new perspectives.
Creating a sense of ownership and responsibility
Employees should be clear about the role they are expected to play in the process of innovation. It is suggested to clearly communicate the actions you want employees to adopt.
Make space for innovation to occur
It is very important to build a protective space around the innovators that is preventing policies or other pressures from interfering with the creative process, and giving innovators the resources required to get results.
Analyze the best ideas and projects thoroughly
It is very important for the management to recognize employee’s idea, as it helps to develop greater interest in their jobs, as well as a deeper involvement and commitment to the company. Seeing things through shows a commitment to innovation and provides success stories to point to.
Celebrate and reward work that leads to innovation
In any organization different people are good at different things. So, when people are recognized for their creativity, they are more likely to work toward organizational achievement in innovation.

