Industrial relations deals with human behaviour and management of personnel in an organizational setup. The various factors that influence the relationship between the administration and the employees in an organization are as follows:
Factors Affecting Industrial Relations
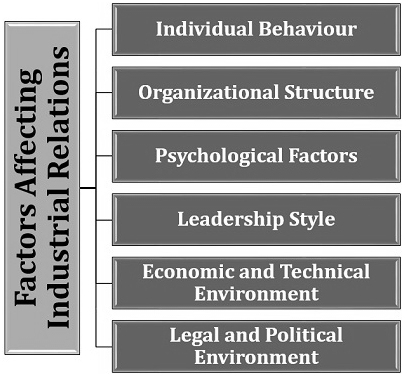
- Individual Behavior: This explains that every person has a different perception, background, skills, knowledge, experience, and achievements which influences an individual’s behavior.
- Organizational Structure: The hierarchical structure creates more formal relationships among the employees belonging to different hierarchical levels in an organization.
- Psychological Factors: This explains an employee’s attitude and mentality towards the employer and the given task. And the employer’s psychology towards the workers can be positive or negative.
- Leadership Style: Every manager possesses certain leadership traits and different styles to function even in a formal organization to generate team spirit and motivate the employees.
- Economic and Technical Environment: Organizations need to restructure the task of the employees including their work duration, conditions, and wages for dealing with the changes in the economic conditions or in their behavior, attitude, adapting spirit, etc.
- Legal and Political Environment: The legal framework and political circumstances influence the organization and its industrial relations contributing to the framing of rules, rights, authority, powers, and responsibilities of all the parties of the organization.
Parties Involved in Industrial Relations
The different persons holding distinct positions in the organization and the external or internal associations involved in the process of building strong industrial relations can be bifurcated into the following two categories:
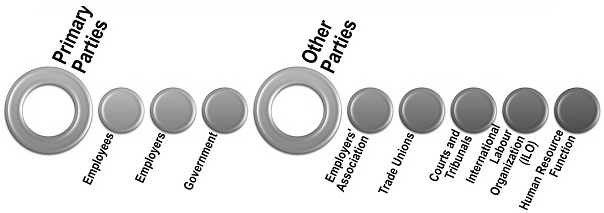
Primary Parties
Those persons or associations which are directly associated with or influenced by the functions of industrial relations are as follows:
Employees
- Employees share their views, suggestions, ideas with the management to improve the business operations and become a part of organizational decision-making, and ensuring the betterment of the working conditions
Employers
They are responsible for:
- Providing a good work environment for the employees and taking strategic decisions such as mergers, acquisitions, or shutting down of the organization, etc.
- Motivating the employees to give their best and gaining their trust and commitment.
- Improving the overall efficiency and ensuring effective communication among the employees and the management.
Government
Government started regulating the industrial relations through labour courts and tribunals, for the following reasons:
- Safeguarding the interest of both the parties.
- Ensuring that both the employer and the employee, abide by the legal terms and conditions.
Other Parties
The parties which impact the industrial relations within an organization are as follows:
Employers’ Association
- Employers Association refers to an authoritative body, formed to protect the interest of the industrial owners.
- They represent the owners in collective bargaining with the employees or government, national issues, and provide insight into employee relations in an organization.
Trade Unions
- Trade Unions mean when the workers unite together to form an association and elect a representative among themselves and to raise their demands in front of the management.
- They demand better working conditions and higher job security for the workers by safeguarding the interest of the employees by demanding control over the decision-making at various levels.
Courts and Tribunals
The judiciary includes the ‘courts’ to resolve the legitimate conflicts and the ‘judicial review’ to administer the justice of the constitution. These courts and tribunals play an essential role in the settlement of industrial disputes by eliminating the possibilities of Judicial flaws, conflicting judgment, poor evaluation of penalty, and Confusing terms and conditions.
International Labor Organization (ILO)
International Labor Organization aimed to look into matters like Worker’s compensation, employee’s work duration and days, women employment, employee’s safety, security, and medical facilities with maternity protection.
Human Resource Function
The human resource department or team acts as a mediator between the organization and its employees for dealing with personnel issues and conflicts. HR professionals address the disputes at the initial level, act as a change agent by bringing a mental revolution and perform the role of an administration expert and a strategic partner.
Scope of Industrial Relations
Industrial relations covers all kinds of formal relationships existing in an organization. The scope of industrial relations can be briefly classified into the following four dimensions:
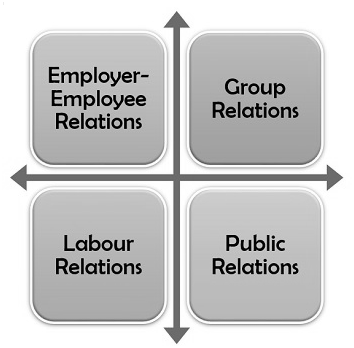
Employer-Employee Relations
The relationship that pertains between the business owner and the employees of a particular company is known as the employer-employee relationship.
Group Relations
The interactions and communication between the workers belonging to different workgroups are studied under group relations.
Labour Relations
In an organization, the relationship shared by the managers and the workers is termed as labour relations.
Public Relations
Public relations or community relations is the interaction and relationship of the organization with the society or external bodies. For long-term existence in the business, every organization needs to maintain cordial public ties.
Objectives of Industrial Relations
Industrial relations hold a high significance in the context of human resource management about addressing the industrial disputes in an organization. The various other goals of carrying out such practices are as follows:
- Handling Grievance: Industrial relations aim to maintain a cordial relationship between the management and the employees by setting up a mechanism to address the grievances of both parties.
- Mental Revolution: It emphasizes on transforming the way of thinking of both the management and the workers. The employer must value the worker’s contribution towards the organization and the employees must respect the authority of the management.
- Employees’ Rights Protection: Under industrial relations, various acts and associations were formed to safeguard the rights and interests of the employees.
- Contract Interpretation: Industrial relations emphasizes on providing proper training to the supervisors and the managers on the labour law contracts to clarify any misunderstanding.
- Boosting Morale: Industrial relations emphasize on building employee’s confidence and boosting their morale to perform better than before.
- Collective Bargaining: The worker’s representative and the management put up their proposals in front of each other and negotiate over the same to reach a mutual decision written in a collective bargaining agreement.
- Increasing Productivity: Industrial relations aims at improving the efficiency and productivity of the organization by ensuring employees’ long-term retention.


