GPR is a major redesign of business processes to achieve improvements in various measures of performance, such as cost, quality, service and speed. Government Process Re-engineering (GPR) has evolved from applying Business Process Re-engineering (BPR) concepts to Government Services. GPR may address all or some of the service quality attributes identified for the government service. BPR enables governments to achieve improvement of performance and application of IT on reengineered processes and which will yield better results for stakeholders. In order to leverage the full advantage of the BPR exercise, suitable IT enablement of the re-engineered processes should also be undertaken.
The “Government Process Re-engineering” (GPR) enhances operational efficiency in administration and service delivery. The knowledge of GPR enables government personnel to improve government functioning through
- Improved citizen focus and experience,
- Minimized process complexity, cost and service delivery time
- Increased transparency levels,
- Reduced administrative burden,
- Adoption of best practices
It is also important to get employee and customer feedback, to understand what is the real requirement of the system and its greatest priority.
Successful GPR requirement
- Innovativeness – Innovative thinking and coming up with solutions rather than replicating the manual system should be focused
- Transformational – It should bring about a drastic improvement in the quality of services provided
- Rational data requirements – Sometimes information needed is rarely used. Hence, justifiable data should be asked.
- Usage of existing data efficiently – Sometimes information asked, is already available with the Government like Date of birth which can be done away with.
- Differentiate between a government rule and procedure – Some procedures can be completely revamped through the use of IT. Like date of birth document are not needed if the access to birth data is provided to the concerned officials requiring this proof.
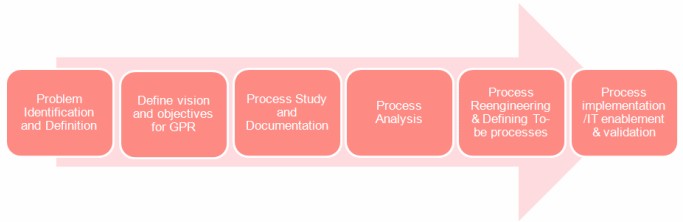
Stages of GPR – GPR consist of various stages and whose first step, is the identification and statement of the problem in the current process scenario. This is followed by the definition of the vision and objectives of GPR. Before setting out on process re-engineering, the existing processes should be studied and documented. During this phase, data is also collected from the different processes, to understand the processes better and to obtain baseline metrics.
The processes thus documented are analyzed using various tools and methodologies, to identify improvement opportunities. This will include identification of value adding / non value adding activities, process complexity and process metrics. During the re-engineering phase, the new processes are designed based on the process re-design drivers. This may involve rework, redesign, outsourcing or replacing of processes / sub processes. The new processes thus defined are implemented, with IT enablement (in most cases). The implementation phase may require changes in the legal framework governing the processes, and change management efforts to smoothen the roll-out.
Important Aspects of Reengineering Process
Experts the skills and knowledge of the process and reengineering should be appointed and consulted about the findings and then the scope and expectations should be clearly described.
- Executive support, sponsorship and required resources should be also be ensured.
- Observation regarding both internal and external environmental forces need to be taken.
- The plan of action should be documented in a charter with clearly defined scope, expectations, measures of success and estimated resource requirements.
- Define an ideal process and develop alternatives and use process benchmarking to find the best practices currently employed by others.
- Communicate recommended plans to all stakeholders and sponsors.
- Update with the improvements anticipated within the project’s goals and objectives.
- Communicate the results and revise goals and objectives.

