Forward pass can be defined as an essential and critical project management component in which the project team leader determines the early start and early finish dates for all of the uncompleted segments of work for all network activities.
The determination of the early start date and early finish date allows for the earliest possible allocation of the resources that may be required for completion of the project and the activities contained within. This primarily refers to the allocation of the project team and the expenditure of their resources, as well as the allocation and expenditures of labour hours. The Early Start (ES) and Early Finish (EF) use the forward pass technique.
Forward pass is a single part of the Critical Path Method used in project management. When conducting a forward pass generates a numerical value in days for the early start and early finish for each task in the project. You are then required to record all this visually on a network diagram, thereby helping the Project Manager determine which tasks in the project can experience a delay and still complete on time without putting risk with the project’s current baseline completion date.
Calculating ES and EF
Steps involved in calculating Early Start and Early Finish date
- Allocate an ES of zero to each of the initial tasks
- Calculate the EF of each initial task by adding the task duration to the ES
- Identify the next task on the network diagram starting at the top of the diagram where this task should come right after the initial tasks. The ES of this task will be the EF of the task that precedes it. In case multiple tasks precede it, then the ES is equal to the longest EF of the immediately proceedings tasks. The EF of this task is equal to the ES plus the duration of the task.
- Repeat the above step for each remaining task in the diagram.
We can calculate the earliest completion by considering the longest EF from the last task in the diagram. In case multiple tasks feed into the completion node then the earliest completion is the longest EF of the tasks that feeds into it. Here, earliest completion helps the project manager to find the best case scenario for finishing the project on time. In order to find the Early Start of an activity, consider factor in all its dependencies and see its earliest start date.
Illustration: Note, the durations of the activities are specified in weeks
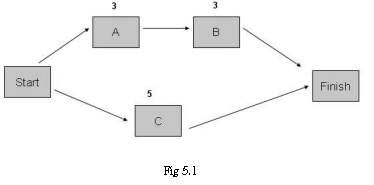
Early Start (ES) for Activity B = 4 weeks
Explanation: B comes after A and it starts on week 1 and finishes on week 3. So B can start at the earliest is week 4. Therefore, ES = Duration of preceding activity + 1
Early Finish (EF) is the earliest calculated time an activity can end, given by
EF = ES of the activity + Activity Duration – 1
EF of activity B = [(4 + 3) – 1] = 6 weeks.
Note – Late Start (LS) and Late Finish (LF) use the backward pass technique. Here the backward pass method is used for calculating backward to see how much an activity may slide without affecting the finish date.
Late Start (LS) is the latest time an activity may begin without delaying the project duration.
LS = Float to the activity + Early Start
Since Activity B is on the critical path, therefore float of activity B is zero. Since Activity B’s ES = 4. Hence, LS = (0 + 4) = 4 weeks. So if an activity has a float of zero, then ES and LS will be the same.
Late Finish (LF) latest time an activity may be completed without delaying the project duration.
LF = (Activity’s LS + Activity Duration) – 1.
LF of Activity B = (4 + 3) – 1 = 6 weeks. Since activity B has a zero float, therefore, EF = LF.
Thus, if float of activity is zero, ES = LS and EF = LF.

