Environmental resources-atmosphere, water, forest, land are natural resources which posses two distinguishing features as compared to other natural resources. They are regenerative in the sense that they are not depleted if we do not use them beyond their natural regenerative levels. The atmosphere and water resources can take some pollution loads without being adversely affected. These environmental resources provide public goods and private goods and services. Public goods have two distinguishing properties as compared to private goods i.e. they are non rival and non exclusive. So private markets are inefficient in allocating public goods as it is difficult or rather, nearly impossible to use market based price systems
Environmental goods have three other major properties-(a) they are irreversible i.e. the decision to use an environmental resource is irreversible. Once used, we will have to wait for the natural regenerative process, which can occur in an economic or in a geological time frame. (b)uncertainty: there is always uncertainty about the outcome of using an environmental resource .For instance, during the green revolution in India in the 1960’s,several high yielding varieties of seeds were introduced .Technological advancements also led to the introduction of fertilizers and pesticides which improved the harvest .However, this supposedly breakthrough improvement was short lived.
Soon, excessive use of subsidized fertilizers led to the soil pollution, lowering of the water table and eventually a massive decline in agricultural harvests. This could not have been prophesied, using any technique, and therefore provides testament to the fact that the outcome of using environmental resources is always uncertain.(c) Uniqueness-some environmental assets are unique in the sense, that they have some existence value. In other words people will be willing to donate some portion of their income for their preservation .For instance, even a person who doesn’t live in Africa may donate for conservation of an African rainforest. Environmental conservationists in India may debate or discuss ways and means to protect blue whales and prevent their imminent extinction.
Human Society was powered solely by biomass till a few centuries ago that is, by biological material from the living or recently dead organisms .For instance, our muscles (powered by energy from the food we eat) or fire from burning wood .A living organism maintains its internal order and the entropy level of it’s internal system by trapping matter and energy drawn from the outside environment to continuously replace the dead tissues with the new. While an organism secures nutrients to construct and maintain its physical structure, it requires energy to run its basic life processes. Without continuous input of energy, an organic system will stop functioning and the organism will move along a positive entropy gradient until it dies.
Energy can be described as the ability to do work, which can be used to move an object physically against an opposing force over some distance. Energy can also be described as stored work. For example, if a piece of stone has been moved away from the centre of the earth ,work has been done against the gravity of the earth which is equal to the force applied to the stone and multiplied by the distance moved. The stone has acquired potential energy which is converted into kinetic energy (energy of motion) when the stone falls down. In the strict physical sense, mechanical work always involves movement of one body relative to another. Similarly fossil fuel, either coal or hydrocarbons, is a chemical energy resource which under certain conditions can be converted to heat energy (for example fossil fuel burnt to raise steam from water in a boiler).Heat Energy can be transformed into mechanical energy in kinetic form with the help of a mechanical device (for example steam is used to drive a piston which in turn pushes an object and drives a wheel resulting in the movement of an object over a certain distance).
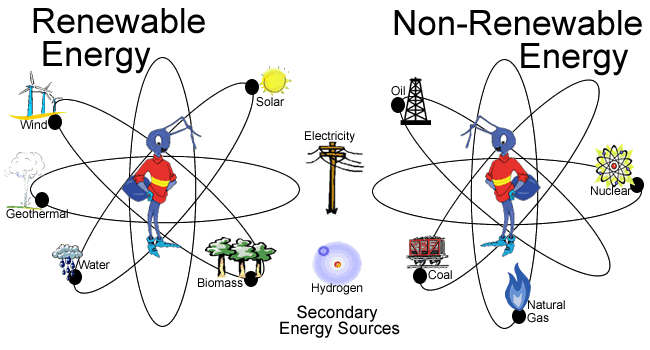
There are nine major types of energy resources. They fall into two categories: nonrenewable and renewable. Nonrenewable energy resources, like coal, nuclear, oil, and natural gas, are accessible in limited supplies. This is usually due to the long time it takes for them to be replenished (a geological time frame, perhaps thousands and thousands of years). Renewable resources are replenished naturally and over relatively short periods of time. The five major renewable energy resources are solar, wind, water (hydro), biomass, and geothermal.