Certify and Increase Opportunity.
Be
Govt. Certified E-Commerce Professional
E-Payment process and types
Electronic payment methods are the payments made electronically rather than by paper (cash, checks, vouchers, etc). It enables serving customers faster and more cost effectively even though the payment and settlement process is a potential bottleneck in the fast-moving E-commerce environment. It can also be defined as a financial exchange that takes place online between buyers and sellers. The content of this exchange is usually some form of digital financial instrument (such as encrypted credit card numbers, electronic cheques or digital cash) that is backed by a bank or an intermediary, or by a legal tender.
E-payment Factors
- Decreasing technology cost – The technology used in the networks is decreasing day by day with increase in reliability and throughput, which is evident from the fact that computers are now available at lower costs and cost of connecting and using the internet is also reducing across the world.
- Reduced operational and processing cost – Due to reduced technology cost the processing cost of e-payment activities becomes very less also saving on both paper and time.
- Increasing online commerce – The above two factors have lead many institutions to go online and many others are following them.
E-payment Need
Any financial transaction being done through e-payment, has to meet at least the following requirements
- Confidentiality – It makes sure that information is only seen by people who have the right to see it thus, implying usage of a strong passwords.
- Integrity – It ensures that information remains intact and unaltered. This means watching out for alterations through malicious action, natural disaster, or even a simple innocent mistake.
- Availability – It implies having access to information when needed. In other words, it means making sure no person or event is able to block legitimate or timely access to information.
- Authenticity – It ensures that the data, transactions, communications or documents (electronic or physical) are genuine. It is also important for authenticity to validate that both parties involved are who they claim to be.
- Non-repudiation – It refers to identity of either parties or that one party of a transaction cannot deny having received a transaction nor can the other party deny having sent a transaction.
The selection of appropriate e-payment method is crucial for e-commerce website and usually focuses on
- Which methods of e-payment will the business be ready for – credit card, e-check, and e-cash?
- Will traditional payment methods i.e. cash, paper checks be accepted?
- Or will a combination of both traditional and e-payment method be accepted?
- What fees is chargeable by the e-payment service provider?
- Which e-payment service provider has secured and reliable e-payment setup?
E-payment Types
Many new e-payment technologies are available which have evolved as per varied needs of user for doing financial transactions, electronically. Different technologies are discussed as
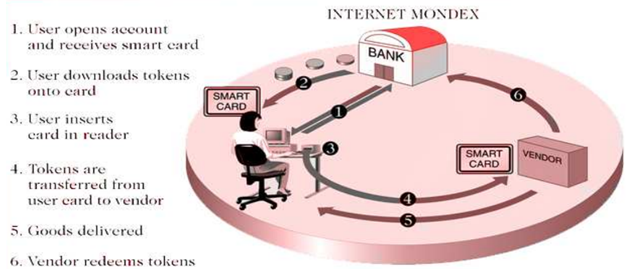
Electronic Cash (or digital cash) – These are Digital forms of value storage and value exchange that have limited convertibility into other forms of value and require intermediaries to convert. It’s process flow can be described as
- Consumer buys e-cash from Bank.
- Bank sends e-cash bits to consumer.
- Consumer sends e-cash to merchant.
- A merchant check with Bank that e-cash is valid (check for forgery or fraud).
- Bank verifies that e-cash is valid.
- Parties complete transaction: e.g., merchants present e-cash to issuing back for deposit once goods or services are delivered.

It has advantages of being more efficient, eventually meaning lower prices with lower transaction costs and hence, anybody can use it, unlike credit cards, and does not require special authorization. But it has disadvantages of no tax trail like regular cash hence, may be used for money laundering and susceptible to forgery.
Few bottlenecks with electronic cash are that it allows spending only once with no divisibility. It is anonymous, just like regular currency hence poses following issues
- Safeguards must be in place to prevent counterfeiting.
- Must be independent and freely transferable regardless of nationality or storage mechanism.
Electronic Wallets – It is similar to physical wallet which stores credit card, electronic cash, owner identification and address. It offers shoppers single, simple and secure means to store cash, electronically. It authenticates the user through the use of digital certificates or other encryption methods, stores and transfers this information also.
It has a value and secures the payment process from the consumer to the merchant thus, making the shopping easier and more efficient also, eliminating the need to repeatedly enter identifying information into forms to purchase. It works in many different stores to speed checkout. Amazon.com one of the first online merchants to eliminate repeat form-filling for purchases using electronic wallet. Various implementations of electronic wallet are
- Agile Wallet – It was developed by Cyber Cash. It allows customers to enter credit card and identifying information once, stored on a central server.
- E wallet – It was developed by Launch pad Technologies. It is an free wallet software that stores credit card and personal information on users’ computer, not on a central server; info is dragged into payment form from e-Wallet.
- Microsoft Wallet – It comes pre-installed in Internet Explorer. All information is encrypted and password protected. Microsoft Wallet Merchant directory shows merchants setup to accept Microsoft Wallet.
The process to use e-wallet is as
- Select the online shop for shopping
- Download a wallet from merchant’s website
- Fill personal and financial information
- Click on the wallet button when, ready to buy

Smart Cards – They are pocket-sized plastic card with a microchip and integrated circuits embedded which can receive input, process it and deliver output. It usually has a service life span of over 10 years. It has not been successful in USA because few card readers are available, but popular in Europe, Australia, and Japan. It’s popularity depends upon
- Number of smart cards that support applications.
- Compatibility between smart cards, card-reader devices, and applications.
There are two types of smart cards in use
- Memory cards
- Micro-processor cards
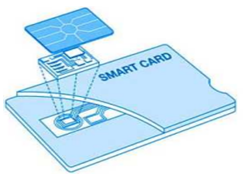

Smart cards offers various advantages of being atomic and debt-free transactions thus, being feasible for very small transactions. Even thought it can be anonymous with being neutral to any currency but has security of physical storage. Smart cards also suffers from disadvantages of high infrastructure costs of readers, etc. and low maximum transaction limit. Due to which smart cards finds applications in ticket-less travel, authentication, medical records, store loyalty programs, licenses and mall parking.
E-Cheque – It is also called as electronic cheque and is like writing a cheque but which is more secure and faster to transact with. An electronic cheque is an electronic copy (scanned image) of a real cheque, which is then transferred by email. In addition to the cheque’s ‘real’ signature, the transfer must be digitally signed using the sender’s private key to authenticate the transfer. Public key cryptographic signatures are substituted for handwritten signatures. E-Cheques pass directly from the payer to the payee, so that the timing and the purpose of the payment are clear to the payee. It is an instruction to financial institution to pay a given amount of money to payee. It is a specially formatted email message sent over the internet having same information as on a cheque.
Credit or Debit Cards – Credit card provides a card holder credit to make purchase up to amount fixed by a card issuer and debit card is linked with the bank account of the user. In B2C based business, they are the most used form of payment system due to high level of convenience and availability with the end-users. Both types of cards involves following players
- Cardholder – person looking to make a purchase
- Card issuer – the bank that issues the credit card to the card holder
- Merchant – business or individual offering goods or services
- Acquirer – often a bank that processes the transaction on behalf of the merchant
- Card Association – Visa, MasterCard, Discover, Amex
Credit Card
Credit card has a preset spending limit as per the user’s credit history and mostly used for internet purchases. Even though it is the most convenient form of e-payment but is also expensive payment mechanism as the end-user has to pay-back the incurred expense, at higher interest rates. Though it is not viable for too small or large amounts
Debit Card
It is used for general purchases and has no spending limit as it is linked with the user’s bank account and all expenses are deducted from the bank account. It is not expensive to use and also allows cash withdrawal from ATMs
Card Processing
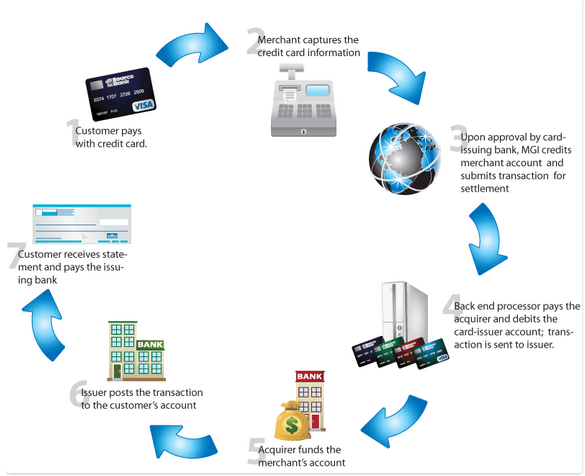
There are four stages in the credit or debit card transaction process
- The Authorization Process – The cardholder requests a purchase from the merchant. The merchant submits the request to the acquirer. The acquirer sends a request to the issuer to authorize the transaction. An authorization code is sent to the acquirer if there is valid credit available. The acquirer authorizes the transaction. The cardholder receives the product.
- The Batching Process – The merchant stores all the day’s authorized sales in a batch. The merchant sends the batch to the acquirer at the end of the day to receive payment
- The Clearing Process – The batch is sent through the card network to request payment from the issuer. The card network distributes each transaction to the appropriate issuer. The issuer subtracts its interchange fees, which are shared with the card network, and transfers the amount. The card network routes the amount to the acquirer.
- The Funding Process – The acquirer subtracts its discount rate and pays the merchant the remainder. The cardholder is billed.
Apply for E-commerce Certification Now!!
https://www.vskills.in/certification/web-development/certificate-in-e-commerce

