In many companies, credit risk management includes a number of organizational units that carry out active credit portfolio management. The significance of active portfolio management is visible most specifically in ensuring that existing credit portfolio structures are more flexible by selling and buying claims in the capital market. As there has been an increase in the importance of active portfolio management and the high degree of responsibility of the managers, these have led some businesses to separate credit portfolio management from risk management in their organizational structures.
Credit plays a vital role in most portfolios and therefore the risk management associated with it is imperative. There are a number of benefits of managing portfolio credit risk.
Reduction of overall credit risk: The culmination of all firm credit risk in a portfolio is not equated to the portfolio risk. Favourable management can decrease the risk of a portfolio to below the total firm risk. Unlike firm-level credit risks, the portfolio credit risk is effected by factors such as distribution of the credit exposures within industry, region etc.
Facilitation of active credit portfolio management: Unlike before, Credit assets can now be offloaded/sold during intermediate periods rather than the end of maturity. While syndicated loans are sold to other participants, the large availability of credit derivatives and securitization are now enabling active credit management. A few basic questions help in evaluating the risks of the portfolio.
- What is the portfolio risk before and after the proposed transaction?
- How does the change in the portfolio risk effect the risk level?
- Which credit assets are to be bought and sold according to changing circumstances?
Enables Maturity Matching: Different credit assets have different due dates. Normally, there are liabilities against the credit assets, and matching of these credit assets and liabilities is necessary for most companies.
Optimizes Liquidity: Most balance sheets have a sizeable debtors’ portfolio. Liquidation of debtors’ portfolio (receivables) is one of the main sources of cash flow to achieve the various obligations such as loan repayments, salary distribution, and settlements with other creditors. Liquidity is better by efficient management of credit portfolio by way of understanding portfolio credit risks. After maturities are fixed by matching the inflows and outflows, liquidity crisis can be avoided. This becomes important when the credit assets are leveraged and have created large amount of external obligations. For example banking institutions depend on the public for creating assets, whereas the non-financial institutions rely on bank credit or public capital debt (bonds, debentures, commercial paper etc.). This provides an inevitable link between solvency, maturity profile and quality of credit assets. Therefore, portfolio credit risks study is of absolute necessity for assessing the liquidity of a business.
Helps sales and marketing: Through good on-hand management of portfolio analysis, the business can display better financials and robust growth. This in-turn serves as good promotion for the company and its sales. Regular evaluation and monitoring of portfolio risk assures that the aggregate risk is managed within the determined range thereby asserting the adequate reserve levels. This evaluation also influences the firm through good governance. Higher risk is avoided if the pertinent shareholder contribution is not there.
Helps in devising portfolio management strategies: A credit portfolio is an assortment of various risk grades of different regions among numerous sectors/industries. A portfolio manager works upon strategies to ascertain that the portfolio risk does not go outside the expected control area. These strategies help the manager be ready to work against all uncertain events through the construction of a balanced portfolio. The impact on portfolio credit risks due to changes in the portfolio mix is also studied. If this portfolio approach is not taken, it becomes very difficult to monitor and control overall risk in the market.
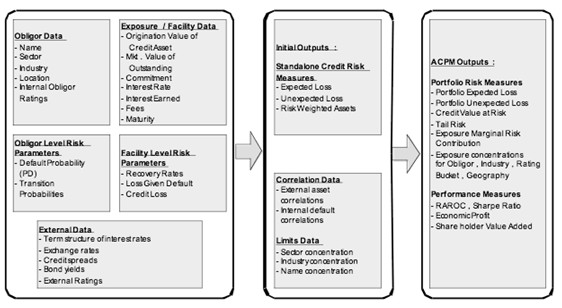
The above structure shows a basic outline of data elements of assessing credit portfolios.
Four major problems have been identified that cause portfolio credit issues. They are detailed in the following sections.

