It consists of following components –
Arithmetic & Logic Unit (ALU) — It is a circuit to perform calculations and logical comparisons.
Registers — data which is processed, is stored here. Each register is “word”-sized and can be accessed at high-speed.
Control Unit or Instruction Decoder — It controls all other parts of the CPU, sending signals in preset patterns to shift data between registers, the ALU and the main data and address buses.
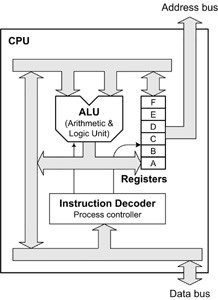
A word is defined by the size of the CPU’s registers and it is the capability of CPU. Thus a “16-bit CPU” has 16bit-sized registers. The external data bus is often the same width as the registers but, it may have different width, depending on the amount of memory that it may access.
Internal cache – Cache memory is a high-speed memory device located between the CPU and main memory. It pre-fetches data and read faster than main memory would allow. The cache closest to the processor is called level 1 (L1) cache and is often built within the CPU circuit itself. Level 2 (L2) cache used to be located on the motherboard but is now integrated onto the CPU and Level 3 cache has also emerged these days
Apply for IT Support Certification
https://www.vskills.in/certification/certified-it-support-professional

