We will discuss two conceptual tools or frameworks available to companies as they search for competitive advantage:
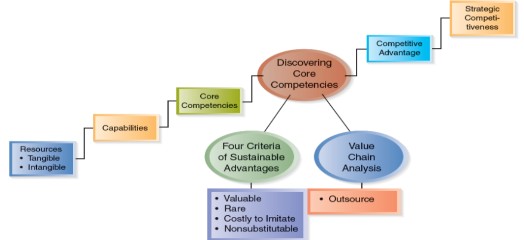
Four criteria which determine which of the company’s resources and capabilities are core competencies, and value chain analysis, a framework for determining which value creating competencies should be maintained, upgraded and developed and which should be outsourced.
Criteria of Sustainable Competitive Advantage
The relationship between resources, capabilities, and the decision point at which managers determine whether or not capabilities are (or are not) core competencies This decision point, which includes four criteria, should be used to determine whether or not a company’s capabilities are core competencies and can be a source of competitive advantage.
However, a short-term competitive advantage is available when company capabilities are valuable, rare, and non-substitutable. The length of time that a company possessing such capabilities can expect to sustain a competitive advantage depends on how long it takes for competitors to successfully imitate the value creating activity or process, or reproduce valued features or characteristics of the product or service.
Thus, the ability to sustain a competitive advantage is dependent on company capabilities being valuable, rare, non-substitutable, and costly to imitate as given below
Core Competencies must be:
- Valuable
- Capabilities that either help a firm to exploit Opportunities
- To create value for customers or to neutralize threats in
- The environment aware
- Capabilities that are possessed by few, if any, current or
- potential competitors
- Costly to Imitate
- Capabilities that other firms cannot develop easily, usually
- Due to unique historical conditions, causal ambiguity or
- Social complexity
- Non Substitutable
- Capabilities that do not have strategic equivalents, such as
- firm-specific knowledge or trust-based relationships
Valuable: Capabilities that are valuable help a company exploit opportunities and/or neutralize threats in the external environment. Valuable capabilities enable a company to develop and implement strategies that create value for customers. For example, Sony uses its valuable capabilities to design, manufacture, and market miniaturized electronic technology to add value for consumers (or to serve as a joint venture partner or perform outsourced activities for other manufacturers who do not possess these valuable capabilities).
Rare: Capabilities are rare when they are possessed by few, if any, current or potential competitors. If many companies have the same capabilities, the same value creating strategies will be selected. As a result, none of the companies will be able to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage. Companies that develop and nurture capabilities that are different from those held by other companies would achieve a competitive advantage.

