Quality Basics
Let’s learn more about Quality Basics. Quality management is the act of overseeing all activities and tasks needed to maintain a desired level of excellence. This includes the determination of a quality policy, creating and implementing quality planning and assurance, and quality control and quality improvement. It is also referred to as total quality management (TQM).
At its core, quality management (TQM) is a business philosophy that champions the idea that the long-term success of a company comes from customer satisfaction. TQM requires that all stakeholders in a business work together to improve processes, products, services and the culture of the company itself. It is an important segment of quality basics.
Quality is a measure of excellence or a state of being free from defects, deficiencies and significant variations. It is brought about by strict and consistent commitment to certain standards that achieve uniformity of a product in order to satisfy specific customer or user requirements.
Quality is linked to the business or service processes used by any organization. A process is the transformation of a set of inputs into outputs that satisfy customer needs and expectations, in the form of products, information or services. Each process in each department or area can be analyzed by an examination of the inputs and outputs for improvements. The output is transferred to somewhere or to someone. Hence, at every supplier/customer interface then there resides a transformation process and every single task throughout an organization must be viewed as a process in this way.
After knowing the process to meet a need, focus on doing the job correctly thus, resulting in a requirement to monitor and control the process.
Process Control
Feedback received from process is used for process control thus, focusing on the input and output of the process for data collection. Every sub-process or task act as an input to next task or as output for previous one. Achieving optimum resources usage by a process though keeping quality output by
- Applying feedback loop to collect data from various process stages so as to apply improvisation
- Re-design the process for data collection, analysis and improvisation as part of the process.
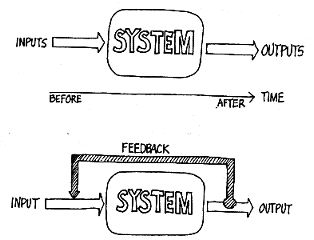
A real-time feedback will initiate improvisation quickly. Tools like control chart helps in data collection and analysis as well.
The control of quality can only take place at the point of operation or production and the act of inspection is not quality control or quality assurance but both are
Quality Management
It serves as an umbrella activity that is applied throughout the software process, involves doing the software development correctly versus doing it over again, it reduces the amount of rework which results in lower costs and improved time to market. It encompasses
- A software quality assurance process
- Specific quality assurance and quality control tasks (including formal technical reviews and a multi-tiered testing strategy)
- Effective software engineering practices (methods and tools)
- Control of all software work products and the changes made to them
- A procedure to ensure compliance with software development standards
- Measurement and reporting mechanisms
Customer View of Quality
From the customer’s perspective, satisfaction after the delivering of the product is the ultimate validation of the product quality. It is clear that the concept of quality must involve customer or, simply put, quality is conformance to customers’ expectations and requirements
Customer views the software as a quality product if it satisfies the below mentioned criteria
- The product received is able to perform the task for which is was purchased
- All the requirements and the needs are being met by the product
- During the transaction they received a treatment which maintained their integrity and respect.
 Stay Ahead with the Power of Upskilling - Invest in Yourself!
Stay Ahead with the Power of Upskilling - Invest in Yourself! 



