Security Market and Emerging Trends
Securities Markets is a place where buyers and sellers of securities can enter into transactions to purchase and sell shares, bonds, debentures etc. Further, it performs an important role of enabling corporate, entrepreneurs to raise resources for their companies and business ventures through public issues. Transfers of resources from those having idle resources (investor) to others who have a need for them (corporate) is most efficiently achieved through the securities market. Stated formally, securities markets provided channels for allocation of savings to investments and entrepreneurship. Savings are linked to investments by a variety of intermediaries, through a range of financial products, called securities.
The securities markets has essentially three categories of participants
- The issuer of securities
- Investor in securities
- Intermediaries
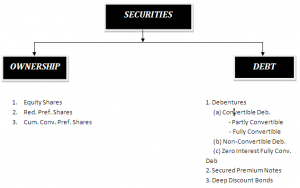
Modes of Investments in securities
- Shares
- Government Securities
- Derivative products
- Units of Mutual Funds
- Preference Shares
- Debentures etc.
Methods of issuing of securities in Indian capital Markets
- Public issue through prospectus: One of the most popular and common methods of issuing is by prospectus. The securities are offered to the investor through detailed statements of terms and conditions known as the prospectus, also known as the offer document.
Contents of a prospectus are as per the Guidelines, includes:
- Name of the company
- Board of directors
- Existing and proposed activities of the authorized issuer
- Issues and paid-up capital
- Name of the merchant bankers
- Lead Manager
- Advisor
- Registrar
- Bankers
- Underwriters
- Minimum Subscription
- Disclaimer clauses
- Terms of the present issue
- Deployment of issue proceeds
- Analysis of financial conditions and result of operations
- Financial information of group companies
- Issues prices and other general and financial information.
2. Offer for Sale: Under this method, the companies do not offer the securities directly to the investor. Instead, the securities are issued to an issue house or a merchant banker who will subsequently offer the sale to the investor. The existing shareholders of a holding company or a foreign parent company may offer to divest their holding to the investors.
3. Issues through Private Placement of securities: The issuing company does not offer the securities to investors in general, instead the securities are offered to selected big institutional clients only. The institutional investor may be selected in compliance with the merchant banker the term and conditions are agreed between the company and the institutional buyer. In case of private placement, SEBI guidelines (2000) are not applicable since there is no public offer involved. Listed companies may adopt private placement method for raising of funds through debt instruments. Also unlisted companies may also adopt this method.