Kanban
Kanban is basically a Japanese term that refers to signboard or visual signals that authorize the movement of items in the manufacturing environment. A Kanban system is a mechanical system that leads to shorter lead times and a reduction in inventory.
Further, it works on the ground that each process on a production line pulls exactly the number and type of components the process requires.
Few generally accepted rules are
- Firstly, downstream processes may withdraw items in the amounts specified on the card.
- Secondly, upstream processes may send items downstream as per quantity and sequence.
- Thirdly, a kanban must partner with each item at all times.
- Lastly, the number of kanbans requires careful evaluation so as to reveal problems and opportunities for improvement.
Kanban Basics:
Card Control
Kanban employs Kanban card wherein, Kan refers to color and Ban refers to the card.
It starts with the customer’s order and follows production downstream. Moreover, the system provides support for external devices such as bar code readers to read the cards and trigger a replenishment signal. Kanbans are generally replenishable and cycle through the system from full to empty, remaining active until they are withdrawn.
Principles
Kanban has its roots in two sets of principles, for change management and service delivery, to emphasize evolutionary change and customer focus. The method does not prescribe a specific set of steps, but starts from existing context and stimulates continuous, incremental and evolutionary changes to the system. Moreover, it aims to minimize resistance to change to facilitate it. There are 6 general practices:
- visualization,
- limiting work in progress,
- flow management,
- making policies explicit,
- using feedback loops,
- and collaborative or experimental evolution.
Boards
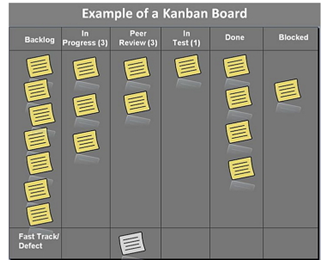
Kanban team does not require a Kanban board to refer to. However, it is the preferred way to see the flow of work, get the participation of the team, and manage work. Moreover, the board shows how work moves from left to right, where each column represents a stage within the value stream.
Metrics
Matrices help Kanban team to move forward, not to penalize someone. Some common metrics include:
- Firstly, Task Completion Rate (TCR
- Secondly, Task Add Rate (TAR)
- Current Task Estimate (CTE) –
- Days to complete = CTE / (TCR – TAR)
Get certified and unlock more opportunities. Practice and Validate your skills to become a Certified Agile Testing Professional Now!

