During the 1980s and early 1990s initial attempts towards e-Governance were made basically focusing towards networking government departments and developing in-house government applications in the areas of defense, economic monitoring and planning These applications focused on automation of internal government functions rather than on improving service delivery to citizens.
The National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) has been formulated by the Department of Information Technology (DIT) and Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DAR&PG). The Union Government approved the National e-Governance Plan (NeGP), comprising of 27 Mission Mode Projects (MMPs) and 8 components on May 18, 2006. The Government has accorded approval to the vision, approach, strategy, key components and implementation framework for the NeGP.
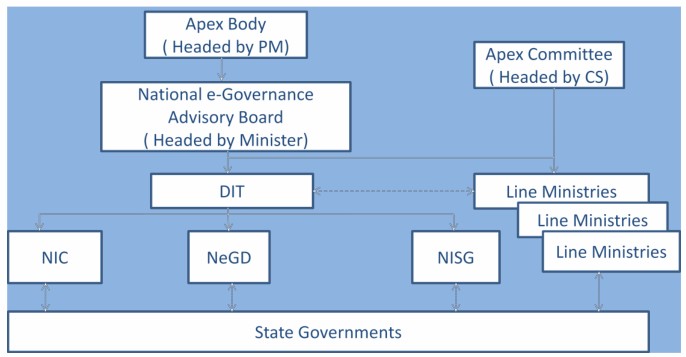
In order to ensure that numerous projects being implemented by the Union and State Government departments are consistent with a broad policy and adhere to common standards, the NeGP established a well defines institutional structure as
Other Key Stakeholders for NeGP are
- Planning Commission and Ministry of Finance: Allocate funds for NeGP through Plan and Non-plan budgetary provisions and lay down appropriate procedures in this regard.
- Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DAR&PG): Responsible for generic Process Re-engineering and Change Management, which are desired to be
- realized across all Government departments.
- Standardization, Testing, Quality and Certification (STQC) Directorate has established itself as a premier organization for Quality Assurance in the field of Electronics and Information Technology (IT) in the country.
- Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), is primarily an R & D institution involved in the design, development and deployment of advanced Information
- Technology (IT) based solutions.
- The Controller of Certifying Authorities (CCA) aims at promoting e-Governance through the wide use of digital signatures
- National Institute for Smart Government (NISG) provides consulting and implementation support to both Central and State Government.
Common Support Infrastructure: NeGP implementation involves setting up of common and support IT infrastructure like State Wide Area Networks (SWANs), State Data Centers (SDCs) and Common Services Centers (CSCs).
The National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) is the most significant initiative taken in India during the last decade to mainstream ICT in governance at both central and state levels. It lays emphasis on creating the right governance and institutional framework within the country, establish the core IT infrastructure, and implement a number of Mission Mode Projects at the central, state and integrated levels.
The plan, consisting originally of 27 Mission Mode Projects (MMPs) and 8 Components, was approved in May 2006. Subsequently, during July 2011, four new MMPs on Health, Education, Public Distribution System (PDS) and Posts were added. The respective ministries and departments in Government of India are responsible for overall formulation, financial approvals and implementation of the MMPs.

