An uninterruptible power supply or uninterruptible power source (UPS), is an electrical system to provide emergency power to a load when the input power source, usually the utility mains, fails. It differs from other power system as it provides instantaneous or near-instantaneous protection from input power interruptions by means of one or more attached batteries and associated electronic circuitry. The on-battery runtime of most is in 5–15 minutes to bring a generator on line, or to properly shut down the equipment.
It is also used to protect computers, data centers, telecommunication equipment or other electrically sensitive equipment where an unexpected power disruption could cause injuries, fatalities, serious business disruption or data loss. UPS units range in size from units designed to protect a single computer without a monitor (around 200 VA rating) to large units powering entire data centers.
Common power problems
Most UPS are also capable of correcting common utility power problems like
Power failure – It is defined as a total loss of input voltage.
Surge – It is defined as a momentary or sustained increase in the main voltage.
Spikes – It is defined as a brief high voltage excursion.
Technologies
UPS are divided into categories based on how many of the above problems they address, and some manufacturers categorize their products in accordance with the number of power related problems they address
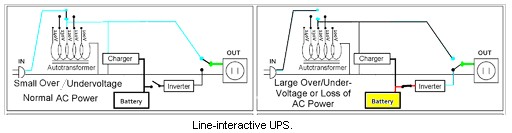
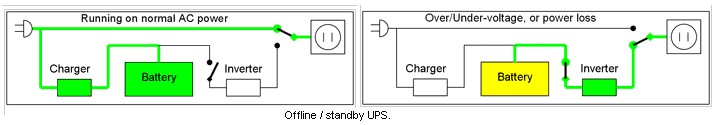
The general categories of modern UPS systems are on-line, line-interactive or standby. An on-line UPS uses a “double conversion” method of accepting AC input, rectifying to DC for passing through the rechargeable battery (or battery strings), then inverting back to 120 V/230 V AC for powering the protected equipment. A line-interactive UPS maintains the inverter in line and redirects the battery’s DC current path from the normal charging mode to supplying current when power is lost. In a standby (“off-line”) system the load is powered directly by the input power and the backup power circuitry is only invoked when the utility power fails. Most UPS below 1 KVA are of the line-interactive or standby varieties which are usually less expensive.
Offline / standby – They have protection time of 0–20 minutes and capacity can not be expanded. It has the most basic features, of surge protection and battery backup. Equipment is connected directly to incoming power. If incoming voltage falls below a specific level UPS supplies power from battery and the switchover time can be 25 milliseconds. The UPS will be designed to power certain equipment, such as a personal computer, without any objectionable dip or brownout to that device.
Line-interactive – Their protection time is 5–30 minutes with good capacity expansion to several hours. It is similar to offline UPS, but with the addition of an autotransformer to increase or decrease the output voltage of the transformer. So, the UPS can tolerate continuous under-voltage and over-voltage surges without battery power. It is popular even in the cheapest UPS. It covers a range from 90 V to 140 V and switch to battery if the voltage goes much higher or lower than that range.
Double-conversion / online– Their protection time is 5–30 minutes with capacity expansion: to several hours. It is must where equipment is very sensitive to power fluctuations. Earlier large installations of 10 kW or more used it, but now it is in 500 watts or less. Its initial cost is slightly higher, but its total cost of ownership is generally lower due to longer battery life. It works well where power anomalies are frequent and protection of sensitive IT equipment is required. The basic technology of the online UPS is similar to standby or line-interactive UPS. But in it batteries are always connected, so that no power transfer switches are necessary. When power loss occurs, the rectifier simply drops out of the circuit and the batteries keep the power steady and unchanged. When power is restored, the rectifier resumes carrying most of the load and begins charging the batteries.
It acts as a barrier between the incoming power and sensitive electronic equipment. While the standby and line-interactive UPS merely filter the input power, but online allow control of output voltage and frequency regardless of input voltage and frequency.
Apply for IT Support Certification
https://www.vskills.in/certification/certified-it-support-professional
 Learn, Certify, Succeed: A Smarter Way to become Job-Ready Now !
Learn, Certify, Succeed: A Smarter Way to become Job-Ready Now !

