Before printing a chart we can preview, as to how it will print by using the print preview option.
Printing Charts
If the chart is embedded on a worksheet, you can adjust where it will print on the page by sizing and moving the chart with the mouse in page break view. To do this, click the worksheet outside of the chart area, and then click Page Break Preview on the View menu. If you’re working with a chart sheet, you can size and scale the chart area, specify how it should be placed on the printed page, and then view it in the preview window. To set printing options for a chart sheet, click the tab for the chart sheet, click Page Setup on the File menu, and then select the options you want on the Chart tab. To move and size the chart area of a chart sheet by using the mouse, you must click Custom on the Chart tab and then click OK to return to the chart sheet. To print an embedded chart without its associated worksheet data, click the embedded chart to select it, and then follow the preceding instructions for chart sheets. You can move and size the chart area of an embedded chart without using the Custom option on the Chart tab (File menu, Page Setup command).
Types Of Charts
There are various types of charts provided by MS-EXCEL, which are discussed as under –
Area Chart
An area chart emphasizes the magnitude of change over time. By displaying the sum of the plotted values, an area chart also shows the relationship of parts to a whole.
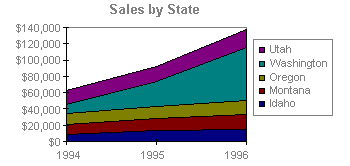
Area Chart
In this example, an area chart emphasizes increased sales in Washington and illustrates the contribution of each state to total sales.
Column Chart
A column chart shows data changes over a period of time or illustrates comparisons among items. Categories are organized horizontally, values vertically, to emphasize variation over time.
2-D column Chart
Stacked column charts show the relationship of individual items to the whole. The 3-D perspective column chart compares data points along two axes.
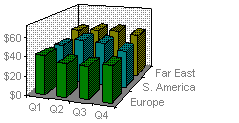
3-D column Chart
In this 3-D chart, you can compare four quarters of sales performance in Europe with the performance of two other divisions.
Bar Chart
A bar chart illustrates comparisons among individual items. Categories are organized vertically, values horizontally, to focus on comparing values and to place less emphasis on time.
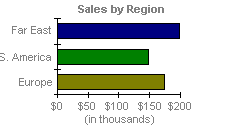
A bar chart
Stacked bar charts show the relationship of individual items to the whole.
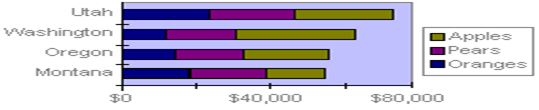
Stacked bar charts
A line chart
A line chart shows trends in data at equal intervals. As shown in the figure below
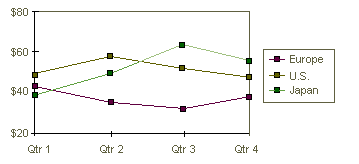
A line chart
Pie Chart
A pie chart shows the proportional size of items that make up a data series to the sum of the items. It always shows only one data series and is useful when you want to emphasize a significant element. As shown in the figure below
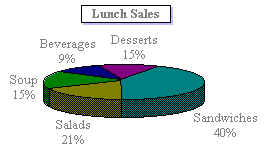
A Pie Chart
To make small slices easier to see, you can group them together as one item in a pie chart and then break down that item in a smaller pie or bar chart next to the main chart.
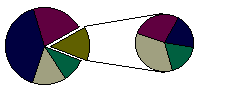
A split pie chart
Doughnut Chart
Like a pie chart, a doughnut chart shows the relationship of parts to a whole, but it can contain more than one data series. Each ring of the doughnut chart represents a data series. As shown in the figure –
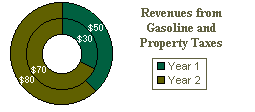
Doughnut Chart
Cone, Cylinder, and Pyramid Chart
The cone, cylinder, and pyramid data markers can lend a dramatic effect to 3-D column and bar charts. As shown in the figure below
A Cylinder Chart
A Cone Chart
A surface chart
A surface chart is useful when you want to find optimum combinations between two sets of data. As in a topographic map, colours and patterns indicate areas that are in the same range of values.
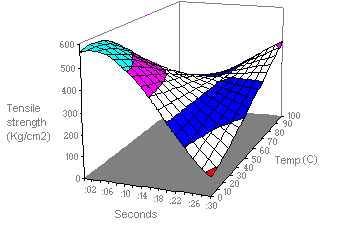
A surface chart
This chart shows the various combinations of temperature and time that result in the same measure of tensile strength.
A Radar Chart
In a radar chart, each category has its own value axis radiating from the center point. Lines connect all the values in the same series.
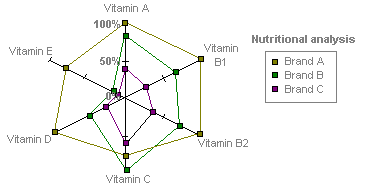
A Radar Chart
A radar chart compares the aggregate values of a number of data series. In this chart, the data series that covers the most area, Brand A, represents the brand with the highest vitamin content.
Bubble chart
A bubble chart is a type of xy (scatter) chart. The size of the data marker indicates the value of a third variable. To arrange your data, place the x values in one row or column, and enter corresponding y values and bubble sizes in the adjacent rows or columns.
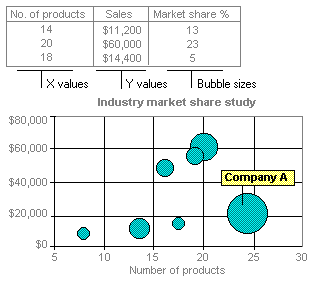
A Bubble Chart
The chart in this example shows that Company A has the most products and the greatest market share, but not the highest sales.
XY (scatter) chart
A xy (scatter) chart either shows the relationships among the numeric values in several data series or plots two groups of numbers as one series of xy coordinates. This chart shows uneven intervals or clusters of data and is commonly used for scientific data. When you arrange your data, place x values in one row or column, and then enter corresponding y values in the adjacent rows or columns. As shown in the figure –
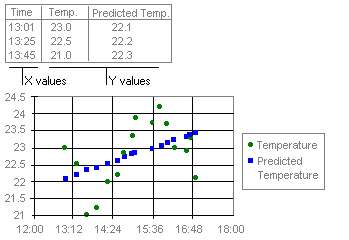
A XY Scatter Chart

