It is an important unit of computer. It is further divided into primary and secondary memory. There is important difference between address number and the contents of the address. The contents stored may be any text, number or any thing but the address at which they are stored is fixed.
Primary Storage Devices
A primary or internal storage section is in all computers and consists of cache, processor register ROM & RAM.
RAM (Random Access Memory)
It provides random selection and usage of memory location to store and retrieve data. It is also called read/write memory because information can be read and can also be written into it. It is a volatile memory; it gets erased as and when the computer is switched off. Whenever a new data is stored, the previous data is erased and new data takes place. It is present in 512/1024 MB.
ROM (Read Only Memory)
A read only memory (ROM) is one in which information is permanently stored. The information from the memory can only be read and it is not possible to write into it. It is non-volatile, i.e. when the power supply is switched off, the contents on ROM do not get erased, and they are permanent and are written only by the manufacturer. The programs, which are always required for running the machine, are stored in ROM. The ROM usually contains the BIOS (Basic Input & Output System) which checks the hardware for proper functioning and in case of problem it stops booting of computer and audio beeps are given. BIOS also load the Operating System into the memory.
Processor Registers
They are located in the CPU to load instructions for execution by the CPU. They function with speed of CPU and hence are the fastest memory. It is present in few KB.
Processor Cache
Processor cache is used for speeding up the data supply to CPU. It stores the most frequently used data from the main memory. When the CPU needs the particular data item, it can simply access the cache memory which is closely located, instead of accessing the much slower main memory. It is present in KB (256/512).
Secondary Storage Devices
Magnetic Tape
The magnetic tape is similar in appearance to an audiocassette. This storage device uses plastic strip coated with the magnetic material as a storage medium. The strip is present in plastic casing. The strip is a plastic ribbon approximately ½ inch in width. The strip is housed in the cartridge. Magnetic tape is slower in accessing the data, but there input and output speeds are high. They are available up to 5120 GB capacity.
Disk Drives
A drive is the name for several types of storage media. They are assigned a drive letter. During start up, drives are typically recognized by System Software (ROM BIOS + Operating System). At the end of this configuration, the appropriate drive letter is identified with each drive. If a drive is not “seen” during start up, it will not be accessible to the operating system. Some examples are
| Storage Media | Drive Letter |
| Floppy Disks Hard Disk CDROM/ DVD USB | A: B: C: D: E: F: G: H: |
Track & Sectors
The disk surface comprises several tracks arranged in concentric circles called tracks which are further subdivided into sectors. The greater the number of tracks, the more is the storage capacity of the disk. When all the sectors, of a track are full, drive starts using the next track.
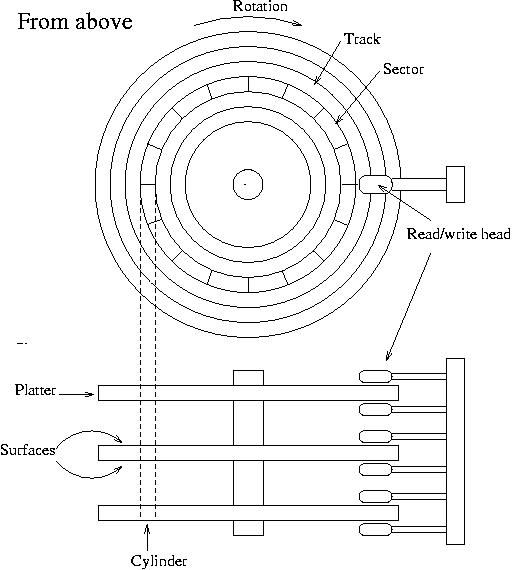
Hard Disk Drive
Hard disk is used for mass storage of data needed for direct access. It is non-volatile random access memory. The disk comes in different sizes such as 3.5, inch, 5.5 inch and 8 inch. Hard disk. It has disk platters mounted on a spindle, on which data is read/written by read/write head. It comes in 250-1024 GB capacity.
Advantages
- Large storage capacity
- Low per MB cost
- Direct addressing leading to random access addition and deletion of records
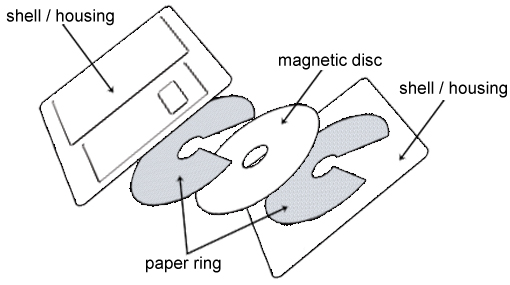
Floppy Disk Drive
A floppy disk is made of flexible plastic material which is coated magnetic substance. Each floppy disk is packaged in a protective paper or plastic envelope from which it is never removed. Floppy disks are mainly used, for the purpose of backup and transportability of data, for small data volumes. Floppy comes in different sizes. 5.25”and 3.5”floppies. Floppy have 1.2 MB and 1.44 MB capacity.
Optical Disk
An optical disk uses optics or light for storage and retrieval of information. The disk is made up of polycarbonate. The disk is coated with a reflective material, whose reflecting property changes when high power laser beam is focused on it. The high power laser beam burns the surface of disk as per the data to be stored on the disk. Low power laser beam is used for reading data from the disk. Most common optical disk is the CD-ROM (Compact Disk – Read Only Memory). CD- ROM has an important property of speed rating, which means the amount of data that can be transferred from the disk. 1X refers to 150 Kbps, 2X refers to 300 Kbps, similarly 4X, 8X, 16X, etc. These days CD- ROM drives have speed rating of 52X. CD-ROM has 700 MB capacity. DVD is high capacity optical disk which can store up to 4.3 GB of data. Blue ray disk is upcoming optical disk technology which can store up to 50 GB data.
Flash Memory
The practical application of this type of volatile computer memory can be seen in USB flash drives, memory cards and portable hard discs. These allow the data to be written to them and can be detached from the system. They can be attached to another computer system to read and transfer the data to it.
Central Processing Unit (C.P.U)
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is responsible for interpreting and executing most of the commands from the computer’s hardware and software. It is often called the “brains” of the computer. The CPU is also known as processor, microprocessor, and central processor. The Central Processing Unit (C.P.U) can be further divide into the following ways.
Control Unit
The control unit is the circuitry that controls the flow of information through the processor, and coordinates the activities of the other units within it. It generates signal as per which the processing is done and is given in MHz/GHz (mega Hertz/ Giga Hertz) .In a way, it is the “brain within the brain”, as it controls what happens inside the processor, which in turn controls the rest of the PC. The functions performed by the control unit vary greatly by the internal architecture of the CPU, since the control unit really implements this architecture.
Functions of Control Unit
A control unit can be described as a sort of circuitry that supervises and controls the path of information that runs over the processor and organizes the various activities of those units that lie inside it.
- It controls the execution of instructions in a sequential order.
- It guides the flow of data through the different parts of the computer.
- It interprets the instructions.
- It regulates the time controls of the processor.
- It sends and receives control signals from various peripheral devices.
Arithmetic Logic Unit
The arithmetic-logic unit (ALU) performs all arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) and logic operations. The data required to perform the arithmetic and logical functions are inputs from the designated CPU registers and operands. The ALU relies on basic items to perform its operations.
Functions of Arithmetic Logic Unit
Almost all the calculations of the computer are done by it. It gets its data from processor register. After the data gets processed, its results get stored in output registers of the arithmetic logic unit.
- It performs integer arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, etc.
- It can also perform bitwise logic operations like AND, OR, XOR, etc.

