Considering the volume of transactions and financial instruments in the fast paced markets, operations would be highly delayed and inaccurate with the proper tools and technology. In order to implement efficient risk management, sound and consistent methods, processes and organizational structures are needed along with specialized IT systems for all five components of the control cycle. The softwares used to show the captured risks, measure, and aggregate into a risk position for the business. In a suitable management application, the features should be used to determine the risk limits, measure the effect of management instruments on the risk position, and monitor the risk positions in terms of observing the defined limits and other requirements.
The organizational processes and structures have to ascertain that risks are measured in a timely manner that risk positions are always matched with the defined limits. It must also make sure that risk mitigation measures are taken in time if these limits are exceeded. It is crucial to ascertain how risk measurement can be combined with determining the limits, risk controlling, as well as monitoring. Furthermore, reporting processes have to be introduced. The organizational structure should ensure that those areas which cause risks are strictly separated from those areas which measure, plan, manage, and control these risks.
IT systems and an IT infrastructure are the essential for efficient risk management. Among other things, a good IT system allows:
- the timely provision and administration of data
- the aggregation of information to obtain values relevant to risk controlling
- an automated warning mechanism prior to reaching critical risk limits.
Credit risk management softwares offer the following core elements of risk management which are derived from the combination of risk management and value management in the company’s capital allocation.
- Data management, including flexible data model, data reconciliation, and data validation
- Integration of risk and finance data
- Credit risk data aggregation
- Flexible analytics engine for calculating PD, LGD, EAD
- Enterprise stress testing
- Model management and governance tools
- Flexible and automated regulatory and internal reporting
- Regulatory and economic capital calculations
- Real-time BI tools Performance and scalability of the core technology (e.g. use of high performance computing and analytics capabilities, such as advanced database technologies, in-memory analytics, and grid computing)
- Collateral management tools
- Linkage to related systems (e.g. ALM, Treasury, Fraud management, Operational risk)
Parties benefit from using the IT applications for credit risk management in the following ways:
- Existing banking credit risk management client-base
- Track record of delivering successful credit risk management projects
- Growth strategy and brand
- Post-sales implementation and support capabilities
- Strategy for and investment in continued innovation in risk technology relating to credit risk management
- Domain knowledge and thought leadership in risk and finance
- Potential volume of credit risk management for banking wins
- Potential value of credit risk management deals (i.e. Tier 1 clients vs. Tier 2 or Tier 3 Clients)
- Scalability of business model (i.e. repeatable sales and delivery capabilities)
- Geographical reach
- Financial strength
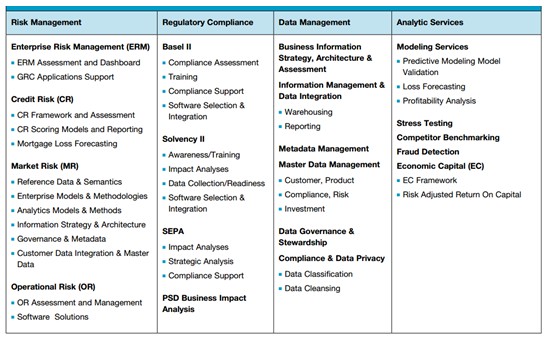
Many businesses till date use unsophisticated credit risk management practices that consist of random processes and basic software tools. Having a standard credit assessment tool is an important part of the credit management process. Using a standard set of software tools helps credit risk assessment and ensure easy and consistent management reporting of the credit risk portfolio. With these applications, managers can understand credit trends, customer sectors, geographies, and the history of both individual customer and portfolio credit risk. A major obstacle towards building an application is the lack of a consistent credit risk assessment process to systemise in the first place. The credit risk policy and credit risk assessment process are many a times missing or outdated, and in need of significant effort to establish the agreement of all stakeholders. To overcome these issues in implementing a software, the producer needs to understanding and systematize the various parameters to be included when processing a credit decision. The following are the steps that must be followed to implement a credit risk tool:-
- Determine credit risk policy
- Determine key control points for sale/shipping
- Design credit assessment process
- Design reporting formats required
- Design tool logic
- Build, test and implement tool
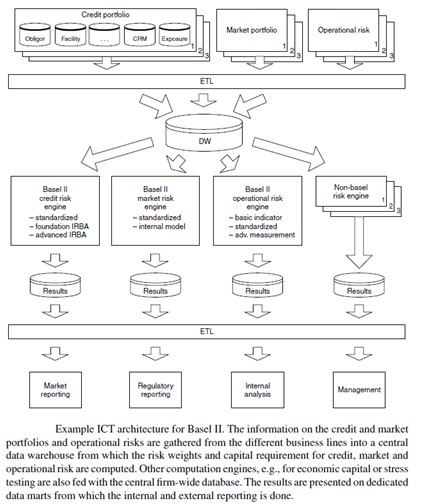
Below is a brief layout of an Information and communication technology (ICT) used to develop a credit risk management system in accordance to Basel II.