Business Process Basics
A business process is a group of tasks which result in a specific service or product for customers. It can be visualized with a flowchart or a process matrix. Business processes are fundamental to every company’s performance and implement the business strategy. Understanding and optimizing the business process is the crux of six sigma.
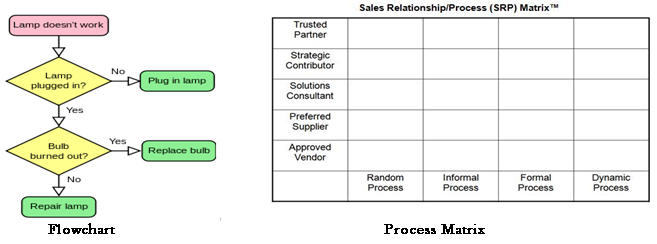
Dissecting and truly understanding root cause for process performance is critical to effective process improvement which can be accomplished by Six Sigma. Each process, have the three elements of inputs, process and outputs that affect its function. A business process is a collection of related activities that produce something of value to the organization, its stakeholders or its customers.
Process Elements
Every process has a start from the state or resources it needs and end where the process need to reach. The intermediate between both is the process logic which makes it possible.
Process Identification
Process to be improved or optimized need to be identified by the process boundaries which indicate the influence and involvement of a process and it’s resources. SIPOC diagrams are usually used for process identification as it provides a top-level view of the process. SIPOC stands for Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs and Customers. SIPOC enables the team to quickly develop a common understanding of the process and it’s key customers and suppliers.
Systems Thinking
Systems thinking entails observing system as whole. The term system is defined as a whole consisting of parts, each of which can affect the other’s properties. The performance of the system is known by how parts interrelate like for a business, the manner in which sales, procurement, manufacturing and distribution relate to each other determines the business performance, instead of individual performance. Systems thinking can be applied in various ways in the Six Sigma project, as
- Systems thinking can be used to launch a high-impact initiative for real root cause areas instead of the symptoms of high level problems.
- It can be used to map out the system dynamics around a mission critical Big Y to optimize, and then identify the various high-leverage daughter projects.
- During the define phase, it identifies the possible negative consequences of optimizing the project Y. Thus, the project team can put avoidance or elimination strategies.
- During the measure or analyze phases the system dynamics of the critical Xs can be identified that affect the project Y that the team has been tasked to optimize.
Owners and Stakeholders
Stakeholders are the entity which has interest in the process or the business and they include the supplier, customer, employees and investors. Similarly the process stakeholder includes the process operators, executive, managers, suppliers, customer and supporting staff like logistics persons. The interest of stakeholders may also vary with time.
Process owners are the individuals within an organization, responsible for coordinating and managing the workflow and activities at every stage of a process. They are also responsible for the performance of a process against the listed goals and measured by key process indicators. they have the authority to make necessary changes to the process and it’s stages in achieving the listed goals.
Project teams having stakeholders and process owners are more effective in achieving the results. Stakeholder involvement is very helpful as they have the detailed knowledge about the process thus, they come out with innovative and impactful process improvement whilst considering the consequences and feasibility of the same.
 Stay Ahead with the Power of Upskilling - Invest in Yourself!
Stay Ahead with the Power of Upskilling - Invest in Yourself! 

