Order fulfillment is the process of storing inventory, picking and packing products, and shipping online orders to customers.
E-commerce order fulfillment applies to both business-to-business (B2B) orders — where large quantities of product are shipped to big-box retailers — as well as business-to-consumer (B2C) orders that are shipped directly to a single shopper’s home.
For B2C orders, the end consumer may place the order on the merchant’s website or through an online marketplace. After the customer completes their purchase, the fulfillment process begins.
The Order Fulfillment Process
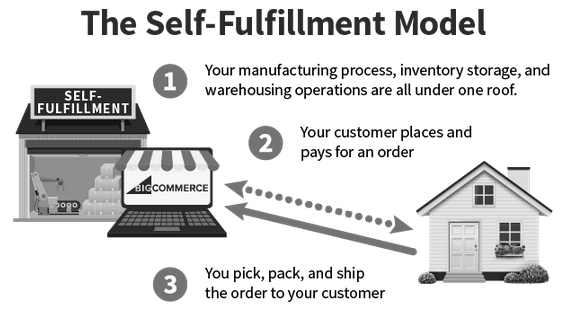
- Step 1. Receiving – Before you can fulfill orders from your online sales channels, you need inventory. If you choose to fulfill orders in-house, your inventory must be on-hand. If you are outsourcing fulfillment, inventory must be sent to the provider that will fulfill on your behalf.
- Step 2. Inventory storage – Inventory storage, also known as warehousing, is the organization and storage of your products. Proper inventory storage will keep your products secure and protected and help give you visibility into what is available to ship to your customers.
- Step 3. Order processing – Once an order has been submitted, it will get processed. These steps involve picking, or the retrieval of items from where they are stored, and packing, or getting the order ready to ship. This may also include instructions on which packing materials to use — boxes, bubble mailers, poly bags, packing tape, bubble wrap, airfill, etc. — or any custom packaging and inserts to create the intended unboxing experience for the end customer. Finally, a shipping label must be added to the package.
- Step 4. Shipping – Once the order has been processed and is ready to send, the merchant must get it shipped. This may involve a run to the local post office or UPS Store, or having a carrier pick up the orders from the fulfillment location.
- Step 5. Returns processing – If a customer returns an order, you must be prepared to process it. They may ship it directly back to you or the fulfillment provider where it will be evaluated. Depending on the item quality, return reason, and your returns policy, the product can either be restocked as available inventory or disposed of due to malfunction.
E-commerce Order Fulfillment Model Types
- In-house order fulfillment. or Fulfill Items Yourself
- Third-party fulfillment.
In-house order fulfillment. or Fulfill Items Yourself
If you’re just starting out and only need to fulfill a few orders a week, it still makes sense for you to fulfill items yourself. This mean you’ll take care of order processing, pick and packing items, attaching labels, and dropping orders off at mail carriers to deliver. You have a lot of responsibility, but with just a few items, you can ensure accuracy and timeliness.
In-house order fulfillment, also known as self-fulfillment, occurs when the merchant completes each step of the fulfillment process internally, without the help of a dropshipper or third-party logistics provider.
In-house fulfillment at this stage typically takes up a lot of valuable time that could otherwise be spent on acquiring more customers, developing new products, and launching marketing campaigns.
Once merchants grow to a certain point and can no longer manage fulfillment alone, they are faced with either outsourcing fulfillment or building out the fulfillment infrastructure themselves.
This model involves
- Securing warehouse space.
- Recruiting and staffing it.
- Purchasing the necessary equipment.
- Licensing warehouse management software.
- Getting workers’ comp and liability insurance.
- And more.
Benefits
- It offers 100% control of inventory and the pick, pack, and ship process.
- It can be low-cost when the business is small because you are just paying for shipping (and doing the work yourself).
- Anyone can do it. You don’t need any contacts (as long as you have space to store products, address labels, and packing resources such as packing slips).
- For businesses shipping significant volume, negotiated shipping rates through FedEx, UPS, and/or USPS can become a competitive advantage.
Disadvantages:
- It is time-consuming. Packing all of the products yourself will take time. As orders increase, this can take up most of your day.
- It is costly as the business grows and can be very burdensome for a young business. You need the following:
- Warehouse space.
- Warehouse equipment.
- Additional staff.
- Order fulfillment software requirements.
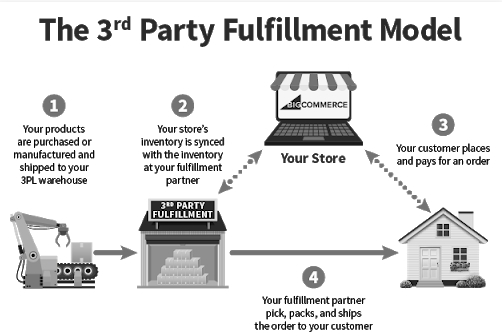
Third-party fulfillment.
Handing off ecommerce fulfillment to a third-party often occurs when a merchant is spending too much time packing boxes and shipping orders, has run out of space to store their inventory, needs more time for strategic projects, and has no interest in managing their own distribution infrastructure.
Because 3PLs work with many merchants and typically operate a number of fulfillment centers, they have the logistical expertise and capacity and are able to negotiate substantial discounted bulk shipping rates from carriers due to the pure volume of shipments they are shipping out each day.
The 3PL’s staff will complete all tasks of the order fulfillment process within their fulfillment center:
- Receiving
- Picking
- Packing
- Labelling
- Returns processing.
- Quality control.
- Other specialized projects.
Each 3PL is unique and has their own services that will vary depending on your needs, including kitting, custom packaging, B2B orders, FBA prep, temperature control or refrigeration, and more.
Advantages:
- Inventory can be purchased in bulk in order to improve profit margins.
- No investment is required for warehouse space/real estate, WMS software, or a workforce to pick and pack orders.
- There is an added convenience of outsourcing the process to a trusted professional.
- Shipping discounts can be much better than if you were to negotiate on your own i.e. Your business ships 5,000 packages per month, but the third-party ecommerce fulfillment company may be handling 150,000 orders per month. They’re going to be able to get better shipping rates with FedEx/UPS than you can alone.
Disadvantages:
- Quality can be compromised.
- You have to do your due diligence: a third-party ecommerce fulfillment company controls your ecommerce businesses’ final handoff of value to your customers. In other words, they have the opportunity to make or break your customer satisfaction levels, which affects the lifetime value of these customers on your business.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping means that the merchant never holds the products they sell in their online store; instead, the products are produced, stored, and shipped by the manufacturer.
When a customer places an order on the merchant’s online store, the order is forwarded either manually or automatically to the manufacturer. Then, the manufacturer dropships the product directly to the end customer.
Hybrid Model
A mix of marketplace and inventory is a hybrid ecommerce model. It’s also called a ‘managed marketplace’ model. It is adopted by most Indian ecommerce players like Flipkart, Amazon, and Snapdeal. Under their marketplace fulfillment services like Snapdeal Plus (SD+), Fulfilment by Amazon (FBA), Flipkart Advantage and Fulfilment by Shopclues, ecommerce players offer inventory storage, packaging & delivering services. But a seller is free to choose self-fulfillment or marketplace-fulfillment.
Under this model, ecommerce players also infuse inventory-led in a marketplace by having operational control over seller entities like Cloudtail (Amazon) & WS Retail (Flipkart) and also by starting their own labels.
Amazon FBA
FBA stands for ‘fulfillment by Amazon’. What is means is that Amazon looks after all of the seller’s stock. When a customer places an order, it by-passes the seller altogether and goes straight to the FBA warehouse. Amazon then picks out the order and delivers it to the customer.
Amazon FBA also handles most of the customer service. They process all customer returns and only the most specific queries get forwarded on to the seller.
To the customer, there is almost no difference between purchasing from Amazon directly and from a person selling their items on Amazon through Amazon FBA. They get the same delivery options, the same returns policy and the same customer service team.
Amazon FBA helps third party sellers grow by giving them access to Amazon’s world-class fulfillment resources and expertise, acclaimed customer services and trusted shipping options and involves following steps
- You send your products to an Amazon fulfillment center or schedule a pickup
- Amazon stores your products – from a single unit to your entire inventory
- Customers order your products from Amazon, often with fast, free delivery through Prime.
- Amazon packs and ships your products from fulfillment center to the customer
Amazon provides customer support on products you sell, ensuring a great experience.

