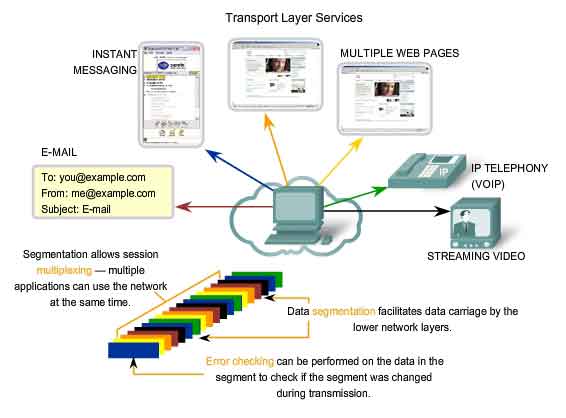
The Transport Layer Services:-
The task of transport layer is to provide reliable and cost effective transport of data from source machine to destination machine. To achieve this goal , the transport layer makes use of the services provided by the network layer.
What is transport entity?
The hardware or software within the transport layer which does the work of making use of the services provided by the network layer is called as transport entity.
Types of Transport Services:-
1. Connection Oriented
- In the connection oriented transport service , there are three phases establishment, data transfer and release respectively.
- Addressing and flow control in transport layer is similar to that in the network layer.
2. Connectionless
- The connectionless transport service also is very similar to connectionless network layer service.
- But, the transport layer has a upper hand. It can improve the quality of service which a network layer cannot do.
- If a transport entity is told that that it’s network connection is abruptly terminated, then it can set up a new network connection to remote the transport entity. Through this new connection , it can ask about which data arrived and which is yet to arrive.
QUALITY OF SERVICE ( QoS)
QoS can be implemented in other layers but it’s actual effect is felt in the transport layer.- The transport layer enhanced the QoS provided by the network layer.
- The transport service may allow the user to specify preffered, acceptable and minimum values of service parameters at the time of setting up a connection.
The typical QoS parameters for transport layer are following:-
- Connection establishment delay:- The time difference between the instant at which a transport connection is requested and the instant at which it is confirmed is called as connection establishment delay. The shorter the delay the better is the service.
- Connection establishment failure probability:- It is the probability that connection is not established even after the maximum connection delay. This can be due to the network congestion, lack of table space or some other problems.
- Throughput:- It measures the number of bytes of user data transferred per second, measured over some time interval. It is measured separately for each direction of data flow.
- Transit delay:- It is the time between a message being sent by the transport user on the source machine and it is being received by the transport user on the destination machine.
- Protection:- This parameter provides a way to protect the transmitted data from being read or modified by some unauthorized parties.
- Priority:- This parameter provides a way for the user to show that some of it’s connection are more important than the higher ones. This is important while handling the congestions.
- Resilence:- Due to congestion, the transport layer spontaneously terminates a connection. The resilience parameter gives the probability of such a termination.
Click here for government certification in Information Technology



6 Comments. Leave new
Good work 😀
Very good, Supreet:)
well structured article !
to the point!
the way you wrote it is quite impressive because it doesnt seem to be a lengthy one , though it is !
enjoyed reading it !
Very well framed and written
Nice work!
Well written