Remember the days when it was such a hassle to view websites on your phone, due to the enormous site space trying to fit on your minute phone screens.
Although with the development of the mobile web many such issues have been overcome, but resolutions still play a big role in the rendering of the webpage on the monitor and how it affects screen real estate.
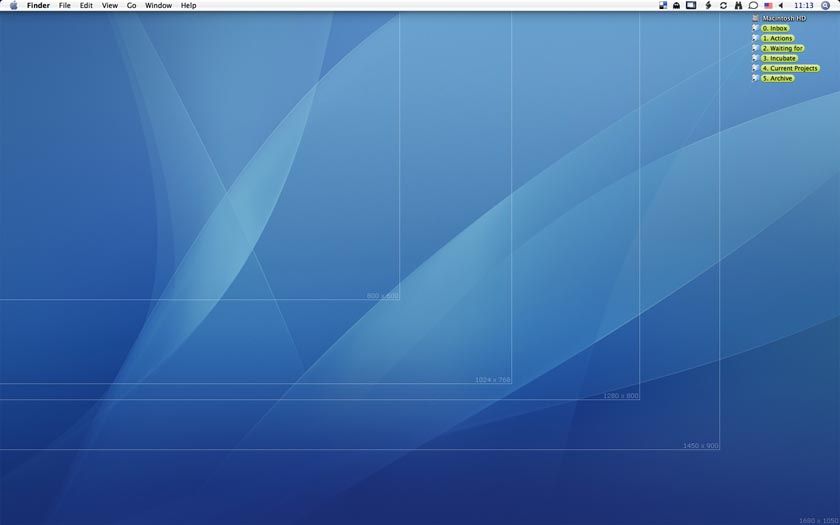
Resolutions affect the design and layout of the web site big time!
Higher the resolution, the more space is available, but smaller the contents appear to the user, and inversely affects the readability.
Think of screen real estate as the canvas on which you paint your website, but the problem is the canvas is different for a variety of devices and settings.
Some users could have a 14” Airbook, whereas some could have the high definition retina display in iPhone 6, whereas other users could have a 21” monitor at home and some might access websites through their 56” Sony smart TV.
Apart from these you also have different resolutions for different devices,
Example for a 21” monitor also you could either have 1280*800, 1024*768 or 640*480.
A higher resolution means you have more virtual space but things appear smaller, on the opposite you have a smaller resolution which means you have lesser virtual space but things appear bigger.
To tackle this problem you could either use JavaScript which detects the browser settings and loads the appropriate the CSS to adapt to the users setting, this method could fail if the script fails to load or is disabled, it’s also cumbersome to create such a wide variety of css style sheets.
Second option is to create a “base” site which would be ideal on different devices, but the drawback is on deciding what resolution should the base site be based on.
The only way to determine this is to know your audience and research about their habits.
Cool Tip: As per W3Schools.com 54% of the users have a screen resolution of 1024*768.



3 Comments. Leave new
Nice …
Nice!
nice…