Even though the defination of management differs from scholar to scholar but in the present era, the concept of management is looked after in the wide areas and its scope is broader. A lot of theories have been developed by the scholars which is called as “Management Theories”. Management theory is generally considered as a collection of ideas assigning general rules on how to manage a business or organization. It is also considered as a Bible for the organizations containing of ideas and paths to be followed from a broader perspective of organization’s goal and its people involvement in achieving the same.
Management theory basically contains of directions on how managers and supervisors relate to their organizations in the terms of its goals, to ensure the implementation of effective means to achieve organizational goals and how to motivate employees to perform their best.
The main objective of management theories is to help increase organizational productivity and service quality if implemented. Many managers don’t use a singular theory or concept by implementation of strategies depending in the workplace. Instead they commonly use a combination of a number of theories, depending on the workplace, purpose and workforce.
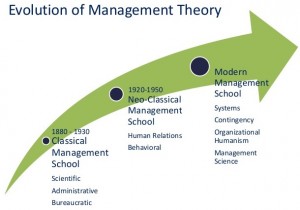
There are various theories of management. Broadly, it includes: Historical Theories of Management and Contemporary Theories of Management.
Historical Theories Of Management:
- Scientific Management Theory: Scientific Management was developed by Freiderick Winslow Taylor, who was popularly known as “Father of Scientific Management Theory”. It is a theory of management that focuses in analyzing workflows. Its main objective is to improve economic efficiency, especially labour productivity. Scientific Management Theory changed the purpose and scope of labour employees. It was one of the earliest intiative to apply science to the engineering and management processes.
The importance of scientific management theory is felt because its approach to management is found in almost every industrial business operation across the world and its influence is also felt in general business practices such planning, process design, quality control, cost accounting, and ergonomics.
The Scientific Management Theory is devised to determine not only the improving efficiency of an organization by systematically improving the efficiency of task completion but also utilizing scientific, engineering, and mathematical analysis. The goal is to reduce waste, increase the process and methods of production, and create a balanced distribution of goods and thereby serves the common interests of employers, employees, and society as a whole.
The four important principles of scientific approach are:-
- Science Not Rule Of Thumb
- Harmony Not Discord
- Cooperation, Not Individualism
- Development of Each and Every Person to His/Her Greatest Efficiency and Prosperity
- Bureaucratic Management Theory: Max Weber embellished the Scientific Management Theory with his bureaucratic theory. Weber focused on dividing organization’s into hierarchies establishing strong and clear lines of authority and control. This theory gave managers legal authority based on their positions in organizations. The theory helped large organization’s to work in a stable manner.
According to him, both bureaucratic leaders and workers are required to obey rules and do only what they are told. The result is that these leaders seldom think of privileged class and found it very difficult to adapt to changing environments and new challenges.
- Administrative Approach:Fayol’s approach rejected the old notion that “managers are born, not made”. According to him,Management is a skill, not a art, which can be acquired, if its principles are understood.
The theory searches to find a way and means rationally to design an organization as a whole. The theory generally calls for a formalized administrative structure, a clear division of labour, and delegation of power and authority to administrators relevant to their areas of responsibilities.
- Human Relations Approach:The approach stressed the need of human interaction and personal relationships in the work place.
Elton Mayo who was an advocate of this theory believed that emotional factors plays important role in determining productive efficiency than logical factors. were far less important than emotional factors in determining productive efficiency”. He concluded that participation in social groups and thereby creating group pressure had the strongest impact on the worker as opposed to organizational structures or demands from management, had the strongest impact on worker productivity.
Mayo’s findings on the theory revolutionized the role of managers in organizations. According to him, managers should be “more people oriented”. Not only the work performed by individual should satisfy their “social needs” but also the company’s productive requirements. The theory echoed for managers to “accept a new role” in their relationship with workers,define a new concept of authority, and help foster a new social order in the workplace. In practice managers were encouraged to consult workers about change, take note of their views, and to show concern for their physical and mental health.
Contemporary Theories of Management:
- Contingency Theory: The contingency theory asserts that managers must take into account all aspects of the current situation and act accordingly on those aspects that are key to the situation at hand while making decisions. Basically, it’s the approach which alerted the managers about their style of functioning depending on the situation.
- System Approach: System Approach to management sought to retain an equal balance between the extremely impersonal Scientific Approach and the individually- focused HR approach. In this approach, all components of an organization are looked as part of one larger system. For this we need to understand the division and department plays within the whole system.
In the 1960, a new approach to management emerged which is commonly known as ‘Systems Approach’. The approach aims to unify the prior schools of thought. This approach advocates include Ludwing Von Bertalanfty, Lawrence J. Henderson, W.G. Scott, Deniel Katz, Robert L. Kahn, W. Buckley and J.D. Thompson.
They viewed organization as an organic and open system, comprising of interacting and interdependent parts, called subsystems. The system approach took upon management as a system or as “an organised whole” made up of sub- systems integrated into a unity.
One of its most important characteristic is that it is composed of hierarchy of sub-systems. That is the parts forming the major system and so on. For example, the world can be considered-to be a system in which various national economies are sub-systems.
- Chaos Theory: The theory recognize that events indeed are rarely controlled. They take into consideration the biological systems while explaining this theory. According to their opinion,systems become more complex, and require more energy to maintain complexity. When energy is expanded, they seek more structure to maintain stability. They believed that the trend will continue until the system splits, combines with another complex system or falls apart entirely.
The impact of any innovation in the relevant field is felt when it is implied and experimented effectively to find out its relevancy. Similarly the advantage of “Management Theory” is felt and realized when it is put into practice benefitting the organizations for its survival and growth.
– Debleena Sinha