Cyber Security refers to the methods that ensure the safety and authenticity of data in the online world. The core functionality of cybersecurity involves protecting info and systems from major cyber threats.
These cyber threats take several forms (e.g., application attacks, malware, ransomware, phishing, exploit kits).
Unfortunately, cyber adversaries have learned to launch automatic and complicated attacks using these techniques – at lower and lower prices. Hence, continuously managing with cybersecurity strategies and operations is a challenge, mostly in government and enterprise networks wherever, showing their most devasting nature, cyber threats often take aim at secret, political, military or infrastructural assets of a nation as whole or its individuals.
Here are some of the most common threats in this domain
Cyberterrorism is the disruptive use of knowledge technology by terrorist teams to additional their philosophical or political agenda.
This takes the shape of attacks on networks, laptop systems and telecommunication infrastructures.
Cyberwarfare involves nation-states using information technology to penetrate another nation’s networks to cause damage or disruption. In the U.S. and many different nations, cyberwarfare has been acknowledged because the fifth domain of warfare (following land, sea, air and space). Cyberwarfare attacks are primarily done by hackers who are well-trained in exploiting the intricacies of pc networks, and operate under the auspices and support of nation-states.
Rather than “shutting down” a target’s key networks, a cyberwarfare attack may intrude into networks to compromise valuable data, degrade communications, impair such infrastructural services as transportation and medical services, or interrupt commerce.
Cyberespionage is the follow of exploitation info technology to get secret info while not permission from its owners or holders. Cyberespionage is most often used to gain strategic, economic, political or military advantage, and is conducted using cracking techniques and malware.
Future of cyber security
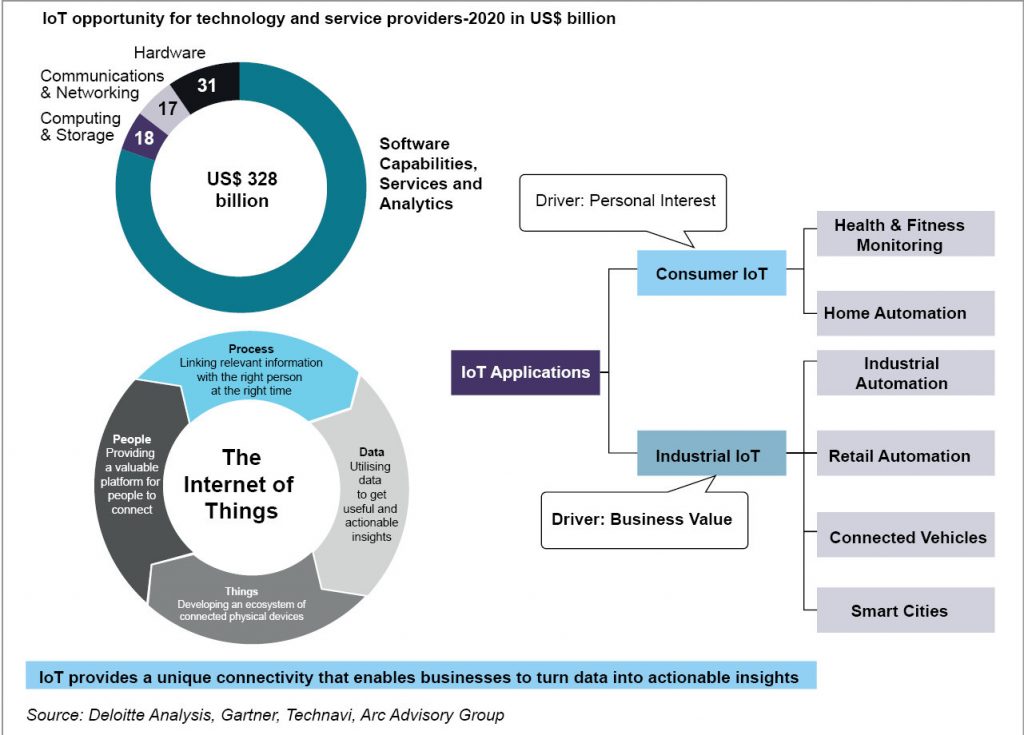
As we all know that the world’s trend is toward Internet of Things where every device in the house will be connected to internet. As you can think, this means an immense opportunities for hackers to gain access to various new devices and as well as a great challenge for people who work for making these devices secure and protected.
The global IoT market can exceed US$ three hundred billion by 2020.
In a NASSCOM study, it was found that the Indian IoT market is projected to reach US $ 15 billion by year 2020, accounting for 5 per cent of the global market (Figure 1).
The IoT market in India is expected to grow exponentially over the next two years. According to 6Wresearch, the Indian IoT market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 28.2 per cent during 2016-22.
The main driving forces of this market are government initiatives, wildfire like acceptance of smart applications, and increasing Internet penetration across the country (thanks to Jio).
The Indian government has launched numerous projects (such as the ‘100 smart cities’ project) and is encouraging organisations to implement IoT. The smart cities project is predicted to play an important role within the overall growth of the market. The World Bank and also the Asian Development Bank (ADB) are expected to supply loans of US$ five hundred million and US$ one billion, respectively, to India for this project.
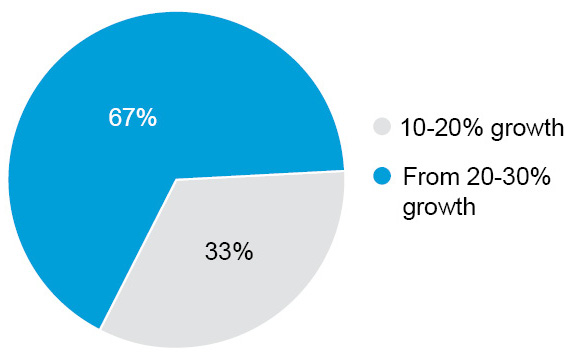
In all the applications of IoT devices in different sectors, industrial applications account for the maximum revenue share in the Indian market owing to their growing usage in energy management, smart buildings, manufacturing, and the environment. There is a common opinion of everyone regarding the future which shows nothing but just the growth of IoT devices. However, there are mixed opinions concerning the proportion of expected growth. Sixty-seven per cent of the respondents expected 20 to 30 percent year-on-year growth (Figure 2).
So here are few most important challenges for IoT security:
Secure constrained devices
Many IoT devices have restricted amounts of storage, memory, and process capability and that they usually ought to be ready to operate on lower power, for example, when running on batteries.
Security approaches that bank heavily on encoding don’t seem to be a decent fit for these strained devices, as a result of they’re ineffective of acting complicated encoding and decryption quickly enough to be able to transmit data securely in real-time.
Authorize and authenticate devices
With such a large amount of devices giving potential points of failure at intervals Associate in Nursing IoT system, device authentication and authorization is essential for securing IoT systems.
Devices should establish their identity before they’ll access gateways and upstream services and apps. However, there are several IoT devices that give way once it involves device authentication, as an example, by using weak basic password authentication, or using passwords unchanged from their default values.
Manage device updates
Applying updates, together with security patches, to firmware or software that runs on IoT devices and gateways presents a number of challenges.
For instance, you will need to regularly keep checking updates of various devices in variety of ways across all the devices connected to the internet. Since all the devices cannot support OTA, or updates without the need to shutdown, so devices might need to be physically accessed or temporarily pulled from production to apply updates.
Also, updates may not be offered for all devices, significantly older devices or those devices that aren’t any longer supported by their manufacturer.
Secure communication
Even if the devices are secured by themselves, ensuing IoT security is a challenge as making sure that the transfer of data across the network between devices and cloud services or apps is also secure. Many IoT devices don’t cipher messages before sending them over the network.
However, best follow is to use transport encoding, and to adopt standards like TLS. Using separate networks to isolate devices additionally helps with establishing secure, personal communication, so that data transmitted remains confidential.
Ensure data privacy and integrity
It is additionally vital that where the info lands up when it’s been transmitted across the network, it is stored and processed securely. Implementing information privacy includes redacting or anonymizing sensitive information before its hold on or using information separation to decouple personally recognizable info from IoT data payloads.
Data that is no longer required should be disposed of securely, and if data is stored, maintaining compliance with legal and regulatory frameworks is also an important challenge.
Secure web, mobile, and cloud applications
Web, mobile, and cloud apps and services are used to manage, access, and process IoT devices and knowledge, in order that they should even be secured as a part of a multi-layered approach to IoT security. As we come to rely more on IoT within our day-to-day lives, IoT developers must consider the availability of IoT data and the web and mobile apps that rely on that information also as our access to the physical things managed by IoT systems.
For instance, in smart cities, IoT infrastructure is responsible for essentials such as traffic control, and in healthcare, IoT devices like pacemakers and insulin pumps. To ensure high accessibility, IoT devices should be protected against cyber-attacks also as physical meddling.
Detect vulnerabilities and incident
Even after one’s best efforts, no one can surely guarantee the shield from hackers. How does one recognize if your IoT system has been compromised? In large scale systems, the complexity of the system in terms of the number of devices connected, and the variety of devices, apps, services, and communication protocols involved, can build it tough to spot once an event has occurred.
Strategies for detecting vulnerabilities and breaches include watching network communications and activity logs for anomalies, engaging in penetration testing and ethical hacking to expose vulnerabilities, and applying security intelligence and analytics to spot and inform once incidents occur.
What effect will government action have on Cyber Security?
Respondents expect bequest governmental and restrictive policies can still be harmful. Technologies like computer science (AI), internet of things (IoT) and blockchain—all of that play considerably within the cyber security space—will further stress policy frameworks.
Bommelaer DE Leusse says that several individuals expressed concern that governments create take actions that undermine cybersecurity. One participant also said that the interests of the government in spying or similar act can affect one’s security. We see a worrying trend during this direction in some components of the globe that prioritize short-run national interests — typically said as ‘cyber sovereignty’ — over longer-term interests and shared responsibility.” Some government actions might prove to be positive.
“There is additionally a situation where, for example, data protection laws, liability, and consumer protection laws are supportive of cyber security strategies, and where governments promote and enable the most efficient solutions,” – Bommelaer de Leusse.
Another trend that alarmed participants in the report is the rise of state-sponsored cyber attacks as the internet is becoming increasingly intertwined with national security. “[An] unsure prospect is that the use of cyber arms and cyberwars to attain political gains between major powers.
This is already happening however it’s unsure whether or not it’ll cause major disruptions to the network and maybe reduce confidence by net users in it,” said one participant in the study.
“Society is changing into more and more addicted to the web, in something from political processes to our economies, and this makes cyber attacks an attractive means that for malicious actors — as well as state sponsored attacks,” says Bommelaer de Leusse.
With no political answer apparent, Bommelaer de Leusse cites the need for international norms to help control this type of state behavior. “Organizations ought to take into account state-sponsored attacks as an opening in their risk assessments. Understanding what assets, whether or not in terms of information or infrastructure, that may be a target for politically intended attackers has to be considered,” she says.
How can I remain safe then?
Here are some points you can keep in mind to help you from easily escaping from some of the most common and obvious ways of security breaches:
- Buy devices that are “secure by design” although this does not guarantee that these devices cannot be tampered with, but the chances will be lesser when compared to completely unsecured devices.
- Use passwords managers to create and save passwords that even you don’t know. This completely rules out any bot or brute-force attack trying to gain access to your account and private data.
- Public Wi-Fi are easiest targets to leak any unencrypted data, so be careful of what you do on public Wi-Fis.
- Become a complete expert in the topic and you can even get hired quickly. This chart clearly shows how much demand there is for people skilled in security.
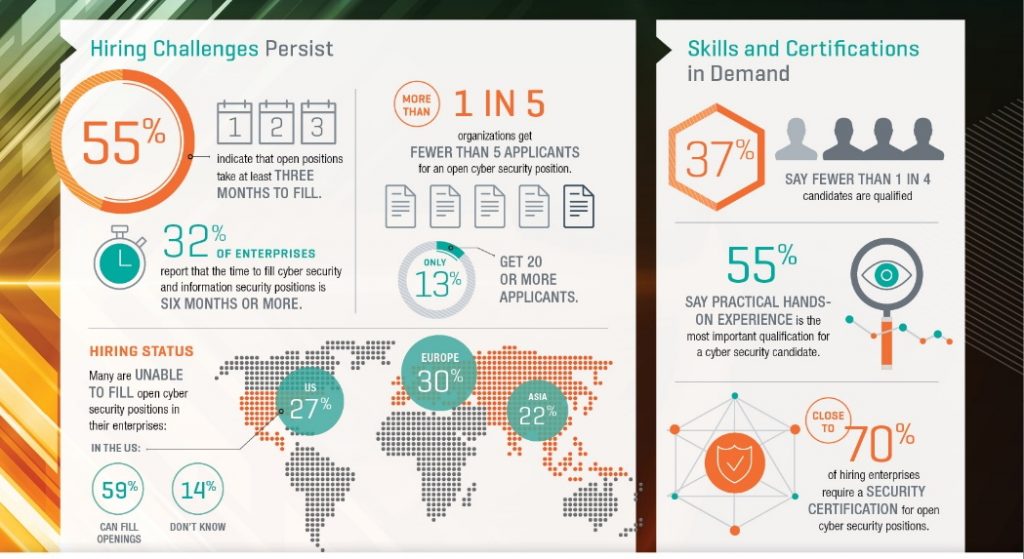
Take a Vskills certification in Cyber Security to move ahead in your career.




2 Comments. Leave new
Nice Article
Wonderful website. Plenty of helpful info here.