Fixed Income Portfolio Management – Passive
Fixed income portfolio management passive is a strategy for managing a portfolio of fixed income securities with a focus on passive management, which means that the portfolio is designed to track the performance of a specific benchmark or index.
The goal of fixed income portfolio management is to generate consistent income while minimizing risk. This is achieved through a combination of diversification, selection of appropriate securities, and managing the duration and credit risk of the portfolio.
In a passive management strategy, the portfolio manager aims to replicate the performance of a benchmark index, such as the Bloomberg Barclays U.S. Aggregate Bond Index, by investing in a similar mix of securities. This approach typically involves lower fees and lower turnover, as the portfolio is not frequently adjusted to try to outperform the market.
Passive fixed income portfolio management is a popular approach for investors who want to achieve stable returns with low risk, as it provides exposure to a broad range of fixed income securities at a lower cost than actively managed strategies.
Indexation
Indexation involves building a portfolio that replicates an observable index. Problems include numerous index components, liquidity is low for many, and bonds mature. The solution is the ‘Cell approach’.
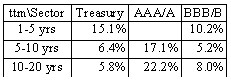
Immunization
In immunization, the manager protects the portfolio value from changes in interest rates. Net worth immunization involves banks frequently having short-term liabilities (deposits) and long-term assets (loans). Objective here is to minimize the inequality in adjustable rate contracts, resale of loans such as mortgages to a third party, and the use of interest rate futures or other derivatives.
Target date immunization aims to guarantee a specific value at a specific point in time. It is often used to match an asset’s future value with a future liability. Interest rate risk can be divided into price risk and reinvestment rate risk. If portfolio duration is equal to planned holding period, then the portfolio is immunized.
Example
A pension fund has a fixed liability of Rs. 1 lakh due in 5 years. Two bonds are available to build a portfolio that matches the liability’s duration.
Bond A: 9% coupon, 5 years to maturity, D = 4.26 years
Bond B: 8% coupon, 8 years to maturity, D = 6.21 years
To generate a portfolio with duration of 5 years, one must determine WA and WB. YTMA = YTMB = 8%
Since WB = 1 – WA, (WA) (DA) + (1 – WA) (DB) = H, where H is the holding period or duration of the liability.
Solving for WA, WA = (H – DB) / (DA – DB)
Hence, the initial position should be 61.8% A and 38.2% B.
One year passes, interest rates have fallen from 8% to 7%. DL = 4
DA = 3.54 DB = 5.62
Duration does not decline at the same rate as time to maturity. An immunization strategy is not purely passive. Must periodically rebalance.
New weights for A and B: 77.9%, 22.1%
Apply for Portfolio Manager Certification Now!!
http://www.vskills.in/certification/Certified-Portfolio-Manager

