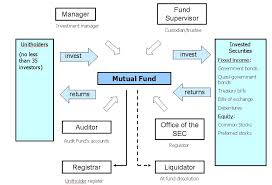
Structure of Mutual Funds
The SEBI (Mutual Funds) Regulations 1993 define a mutual fund (MF) as a fund established in the form of a trust by a sponsor to raise monies by the Trustees through the sale of units to the public under one or more schemes for investing in securities in accordance with these regulations.
These regulations have since been replaced by the SEBI (Mutual Funds) Regulations, 1996. The structure indicated by the new regulations is indicated as under.
A mutual fund comprises four separate entities, namely sponsor, mutual fund trust, AMC and custodian. The sponsor establishes the mutual fund and gets it registered with SEBI.
The mutual fund needs to be constituted in the form of a trust and the instrument of the trust should be in the form of a deed registered under the provisions of the Indian Registration Act, 1908.
The sponsor is required to contribute at least 40% of the minimum net worth (Rs. 10 crore) of the asset management company. The board of trustees manages the MF and the sponsor executes the trust deeds in favour of the trustees. It is the job of the MF trustees to see that schemes floated and managed by the AMC appointed by the trustees are in accordance with the trust deed and SEBI guidelines.
Apply for Mutual Funds Analyst Certification Now!!
https://www.vskills.in/certification/mutual-funds-analyst