Certify and Increase Opportunity.
Be
Govt. Certified E-Commerce Professional
CSS (Cascading Style Sheet)
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a language specifically made for illustrating the appearance of various parts of a web page. CSS gives option to control the text color, fonts style, inter- paragraph spacing, columns sizing and layout, background images or colors and many other visual effects. CSS is used to style web pages, developed in HTML or XHTML
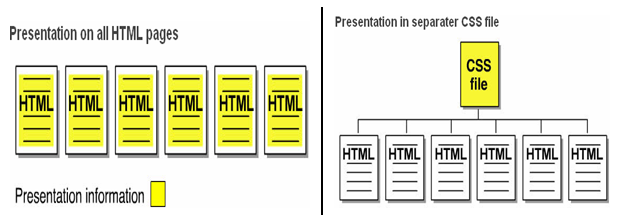
The major advantage of CSS is to customize the style of an entire website without changing each page individually.
A CSS Example
This example introduces CSS and for which the HTML document is needed is given first and then followed by the CSS file.
Webpage.htm:
In your text editor of choice, enter the following markup
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC “-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN”
“http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1-strict.dtd”>
<html lang=”en”>
<head>
<title>Vskills Example </title>
<link rel=”stylesheet” type=”text/css” href=”style.css” />
</head>
<body>
<h1>Vskills Certification </h1>
<div class=”list1″>
<h2>CSS Designer</h2>
<p>CSS designer certification is used to impart CSS certification.</p>
</div>
<div class=”list1″>
<h2>HTML Certification</h2>
<p>HTML certification is used to impart HTML certification.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Style.css:
body {
width: 650px;
margin: 0 auto;
background: #FFF;
font: 12px sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 20px;
}
h2 {
font-size: 16px;
margin-top: 0;
}
.list1 {
margin: 10px 10px;
padding: 20px 20px;
border: 1px solid #F00;
}
Output:

As the figure shows that CSS can be used to stylize the various HTML elements on a web page thus simplifying the process of styling the same.
Including CSS
CSS can be included in a web page in following four ways
Embedded Style Sheets – Embedded style sheets are included between <style> and </style> tags in an web page’s head section as
<style type=”text/css”>
body { font: 12px sans-serif; }
</ style >
External Style Sheets – In it CSS is in a separate document which is linked to an web page by the <link> element with “rel” attribute having “stylesheet” as its value, “type” attribute having ”text/css” as its value and “href “ attribute having the path to CSS file. It is used as
<link rel=”stylesheet” type=”text/css” href=”style.css”>
- rel=”stylesheet” tells the link type —in this case, a link to a style sheet.
- type=”text/css” lets web browser know the type of data to get—a text file, having CSS.
- href points to the location of the external CSS file and has the value of a URL similar to the src attribute in an <image> tag.
Import Rule – It is similar to external style sheet but instead of <link> element, it uses “@import” with “url” attribute storing the path to the CSS file. It is used as
<style type=”text/css”>
@import url(style.css);
</ style >
It can attach external style sheets to an external style sheet but the <link> tag can’t.
Direct Style – Inline styles with the style attribute are used to apply CSS rules directly to an element in an web as
<body style=”font: 12px sans-serif;”>
CSS Components
A CSS style is basically a rule which specifies to a web browser about how to format a HTML element on a web page like a rule to make a headline blue, draw a border around a photo, or create a 250- pixel-wide sidebar box to hold a list of links. A style consist of two elements
- The web page element that the browser formats also called as the selector.
- The actual formatting instructions also called as the declaration block or rules block.
Rules
A selector can be a <h1> or a <h2> tag, a <p> tag having a paragraph of text and declaration block can turn that text blue, add a red border around a paragraph, position the photo in the center of the page as required by the user.
The declaration block also called as rules block consists of property and value pairs separated by ‘;’ and curly braces to surround the block and colons to separate the property and value. The following rule shows the parts of a style sheet and the special characters that separate them.
h2 {
font-size: 16px;
margin-top: 0;
}
Also illustrated in the figure

Rules can be given in any sequence and spacing or line breaks or white space are given for better organization and readability as given in HTML. Thus giving increased maintainability and productivity.
Background Properties
| Property | Description | Possible Values | Examples |
| background-color | Declares the background color. | Valid color names, RGB values, hexidecimal notation. | div { background-color:green; }
div { color:#00FF00; } |
| background-image | Declares the background image of an element. | URL values. | div { background-image:url(images/img.jpg); }
body { background-image:url(img.jpg); } |
Classification and Positioning Properties
| Property | Description | Possible Values | Examples |
| float | Declares whether a box should float to the left or right of other content, or whether it should not be floated at all. | left right none |
div { float:left; }
div { float:right; } |
| visibility | Declares the visibility of boxes generated by an element. | visible hidden collapse |
div { visibility:visible; }
div { visibility:hidden; } |
Dimension Properties
| Property | Description | Possible Values | Examples |
| height | Declares the height of the element. | Lengths, percentages, and the predefined value auto. | div { height:200px; }
div { height:50%; } |
| width | Declares the width of the element. | Lengths, percentages, and the predefined value auto. | div { width:500px; }
div { width:75%; } |
Font Properties
| Property | Description | Possible Values | Examples |
| font-family | Declares the name of the font to be used. Previously set in HTML via the face attribute in a <font> tag. | Valid font family names or generic family names, i.e. Arial, Verdana, sans-serif, “Times New Roman”, Times, serif, etc.
Font family names can be separated by a comma in the same declaration to allow additional and/or generic family names to be used if the preferred font is unable to be displayed. |
div { font-family:Arial; }
div { font-family:Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif; } |
| font-size | Declares the size of the font. Previously set in HTML via the size attribute in a <font> tag. | Lengths (number and unit type— i.e. 1em, 12pt, 10px, 80%) or one of the following predefined values:
xx-small / x-small /small /medium /large / x-large / xx-large / smaller / larger |
div { font-size:70%; }
div { font-size:0.85em; } div { font-size:medium; } |
| font-style | Declares the font style. | normal / italic / oblique | div { font-style:italic; }
div { font-style:oblique; } |
| font-variant | Declares the font variant. | normal / small-caps | div { font-variant:normal; }
div { font-variant:small-caps; } |
| font-weight | Declares the font weight (lightness or boldness) | normal / bold / bolder / lighter / 100 to 900 | div { font-weight:bolder; }
div { font-weight:200; } |
List Properties
| Property | Description | Possible Values | Examples |
| list-style-type | Declares the type of list marker used. | disc / circle / square / decimal | ol { list-style-type:upper-roman; }
ul { list-style-type:square; } |
| list-style-image | Declares an image to be used as the list marker. | URL values. | ul { list-style-image:url(image.jpg); } |
Apply for E-commerce Certification Now!!
https://www.vskills.in/certification/web-development/certificate-in-e-commerce

